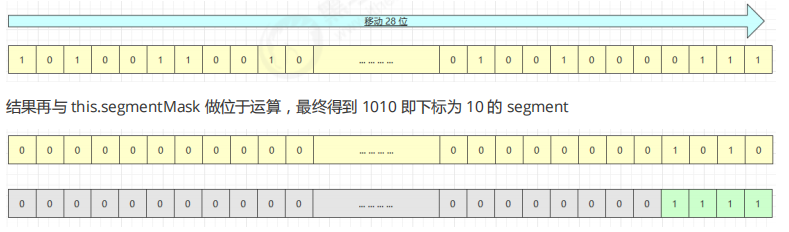
AQS(Abstract Queued Synchronizer) 概述 全称是 Abstract Queued Synchronizer,是阻塞式锁和相关的同步器工具的框架
特点 state属性 独占/共享模式
等待队列
提供了基于 FIFO 的等待队列,类似于 Monitor 的 EntryList
条件变量
条件变量来实现等待、唤醒机制,支持多个条件变量,类似于 Monitor 的 WaitSet
需要子类实现的方法 子类主要实现这样一些方法(默认抛出 UnsupportedOperationException)
tryAcquire
tryRelease
tryAcquireShared
tryReleaseShared
isHeldExclusively
获取锁的姿势 1 2 3 4 if (!tryAcquire(arg)) { }
释放锁的姿势 1 2 3 4 if (tryRelease(arg)) { }
实现不可重入锁 自定义同步器 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 final class MySync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer { @Override protected boolean tryAcquire (int acquires) { if (acquires == 1 ){ if (compareAndSetState(0 , 1 )) { setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread()); return true ; } } return false ; } @Override protected boolean tryRelease (int acquires) { if (acquires == 1 ) { if (getState() == 0 ) { throw new IllegalMonitorStateException (); } setExclusiveOwnerThread(null ); setState(0 ); return true ; } return false ; } protected Condition newCondition () { return new ConditionObject (); } @Override protected boolean isHeldExclusively () { return getState() == 1 ; } }
自定义锁 有了自定义同步器,很容易复用 AQS ,实现一个功能完备的自定义锁
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 class MyLock implements Lock { static MySync sync = new MySync (); @Override public void lock () { sync.acquire(1 ); } @Override public void lockInterruptibly () throws InterruptedException { sync.acquireInterruptibly(1 ); } @Override public boolean tryLock () { return sync.tryAcquire(1 ); } @Override public boolean tryLock (long time, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException { return sync.tryAcquireNanos(1 , unit.toNanos(time)); } @Override public void unlock () { sync.release(1 ); } @Override public Condition newCondition () { return sync.newCondition(); } }
测试一下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 MyLock lock = new MyLock ();new Thread (() -> { lock.lock(); try { log.debug("locking..." ); sleep(1 ); } finally { log.debug("unlocking..." ); lock.unlock(); } },"t1" ).start(); new Thread (() -> { lock.lock(); try { log.debug("locking..." ); } finally { log.debug("unlocking..." ); lock.unlock(); } },"t2" ).start();
输出
1 2 3 4 22 :29 :28.727 c.TestAqs [t1] - locking... 22 :29 :29.732 c.TestAqs [t1] - unlocking... 22 :29 :29.732 c.TestAqs [t2] - locking... 22 :29 :29.732 c.TestAqs [t2] - unlocking...
不可重入测试
如果改为下面代码,会发现自己也会被挡住(只会打印一次 locking)
1 2 3 4 lock.lock(); log.debug("locking..." ); lock.lock(); log.debug("locking..." );
起源 早期程序员会自己通过一种同步器去实现另一种相近的同步器,例如用可重入锁去实现信号量,或反之。这显然不够优雅,于是在 JSR166(java 规范提案)中创建了 AQS,提供了这种通用的同步器机制。
目标 AQS 要实现的功能目标
阻塞版本获取锁 acquire 和非阻塞的版本尝试获取锁 tryAcquire
获取锁超时机制
通过打断取消机制
独占机制及共享机制
条件不满足时的等待机制
要实现的性能目标
Instead, the primary performance goal here is scalability: to predictably maintain effiffifficiency even, or especially, when synchronizers are contended.
设计 AQS 的基本思想其实很简单
获取锁的逻辑
1 2 3 4 5 6 while (state 状态不允许获取锁) { if (队列中还没有此线程) { 入队并阻塞 } } 当前线程出队
释放锁的逻辑
1 2 3 if (state 状态允许了) { 恢复阻塞的线程(s) }
要点
原子维护 state 状态
阻塞及恢复线程
维护队列
state 设计
state 使用 volatile 配合 cas 保证其修改时的原子性
state 使用了 32bit int 来维护同步状态,因为当时使用 long 在很多平台下测试的结果并不理想
阻塞恢复设计
早期的控制线程暂停和恢复的 api 有 suspend 和 resume,但它们是不可用的,因为如果先调用的 resume 那么 suspend 将感知不到
解决方法是使用 park & unpark 来实现线程的暂停和恢复,具体原理在之前讲过了,先 unpark 再 park 也没问题
park & unpark 是针对线程的,而不是针对同步器的,因此控制粒度更为精细
park 线程还可以通过 interrupt 打断
队列设计
使用了 FIFO 先入先出队列,并不支持优先级队列
设计时借鉴了 CLH 队列,它是一种单向无锁队列
队列中有 head 和 tail 两个指针节点,都用 volatile 修饰配合 cas 使用,每个节点有 state 维护节点状态
入队伪代码,只需要考虑 tail 赋值的原子性
1 2 3 4 5 do { Node prev = tail; } while (tail.compareAndSet(prev, node))
出队伪代码
1 2 3 4 5 while ((Node prev=node.prev).state != 唤醒状态) {} head = node;
CLH 好处:
AQS 在一些方面改进了 CLH
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 private Node enq (final Node node) { for (;;) { Node t = tail; if (t == null ) { if (compareAndSetHead(new Node ())) tail = head; } else { node.prev = t; if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) { t.next = node; return t; } } } }
主要用到 AQS 的并发工具类
ReentrantLock 原理 ReentrantLock 支持公平锁和非公平锁,可重入锁
ReentrantLock 的底层是通过 AQS 实现。
非公平锁实现原理 加锁解锁流程 先从构造器开始看,默认为非公平锁实现
1 2 3 public ReentrantLock () { sync = new NonfairSync (); }
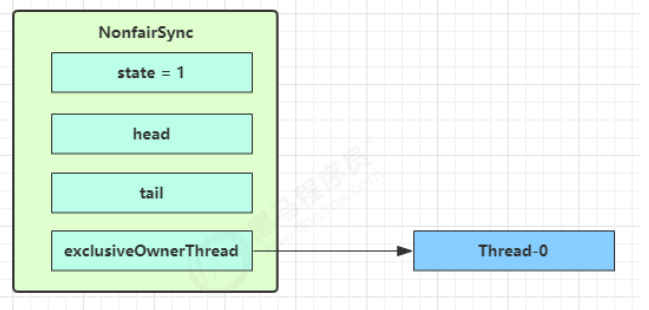
NonfairSync 继承自 AQS
没有竞争时(占有锁) 1 2 3 4 5 6 final void lock () { if (compareAndSetState(0 , 1 )) setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread()); else acquire(1 ); }
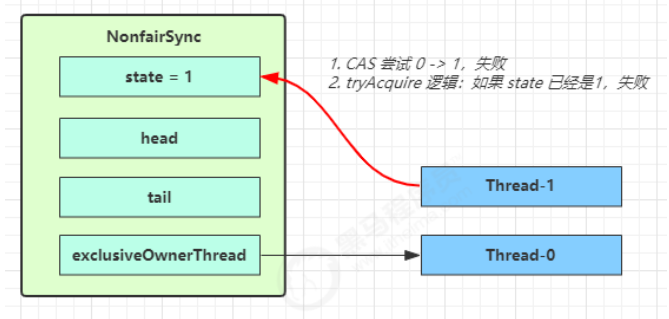
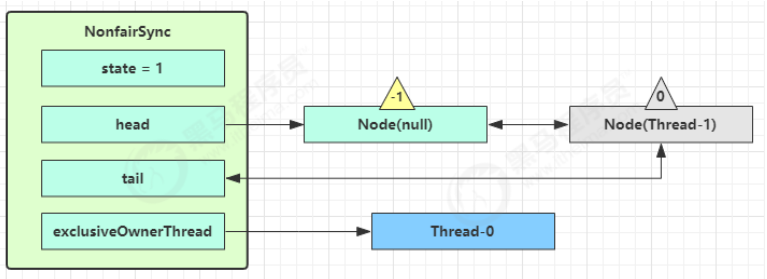
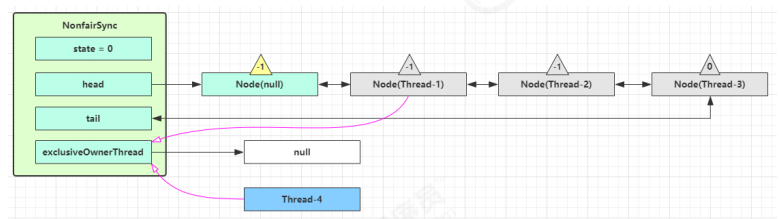
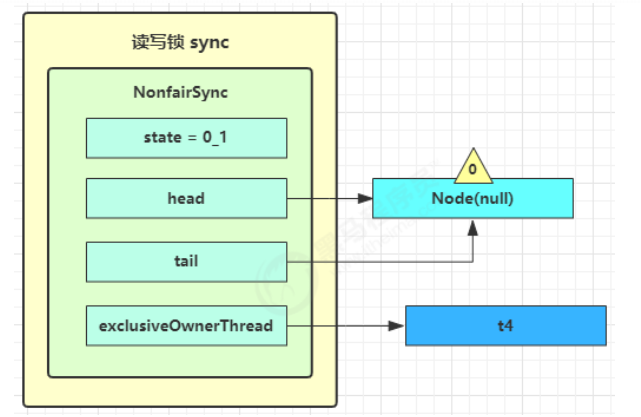
第一个竞争出现时(发生排队)
Thread-1 执行了
CAS 尝试将 state 由 0 改为 1,结果失败
进入 tryAcquire 逻辑,这时 state 已经是1,结果仍然失败
1 2 3 4 public final void acquire (int arg) { if (!tryAcquire(arg) && acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg)) selfInterrupt(); }
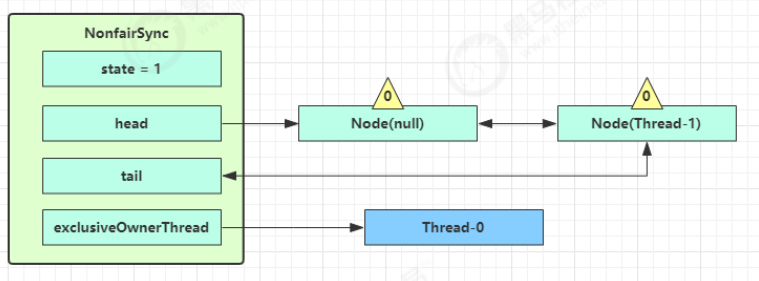
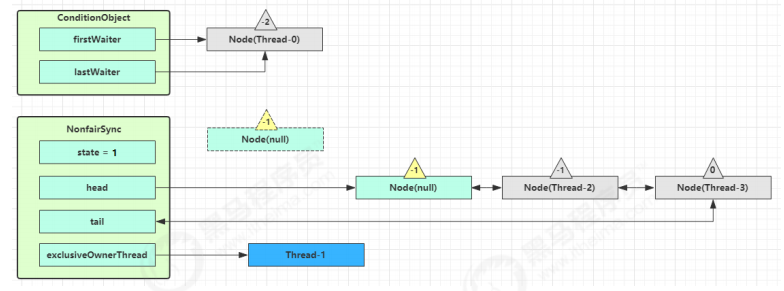
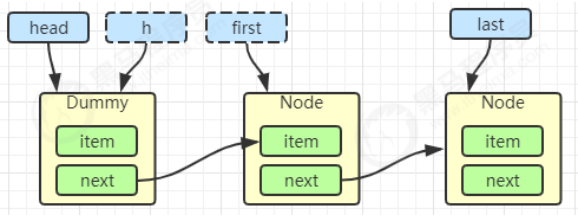
接下来进入 addWaiter 逻辑,构造 Node 队列
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 private Node addWaiter (Node mode) { Node node = new Node (Thread.currentThread(), mode); Node pred = tail; if (pred != null ) { node.prev = pred; if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) { pred.next = node; return node; } } enq(node); return node; }
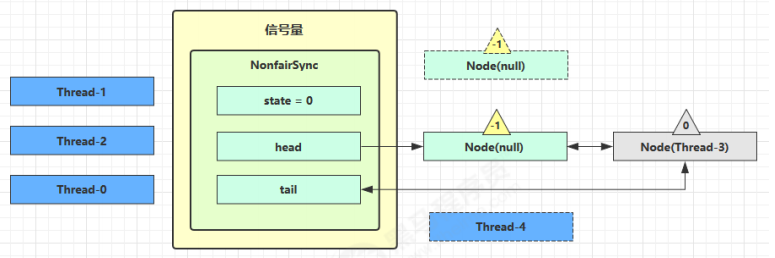
图中黄色三角表示该 Node 的 waitStatus 状态,其中 0 为默认正常状态
Node 的创建是懒惰的
其中第一个 Node 称为 Dummy(哑元)或哨兵,用来占位,并不关联线程
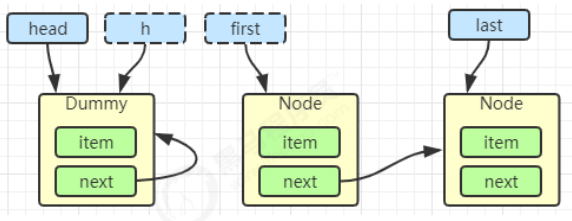
当前线程进入 acquireQueued 逻辑
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 final boolean acquireQueued (final Node node, int arg) { boolean failed = true ; try { boolean interrupted = false ; for (;;) { final Node p = node.predecessor(); if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) { setHead(node); p.next = null ; failed = false ; return interrupted; } if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) && parkAndCheckInterrupt()) interrupted = true ; } } finally { if (failed) cancelAcquire(node); } }
acquireQueued 会在一个死循环中不断尝试获得锁,失败后进入 park 阻塞
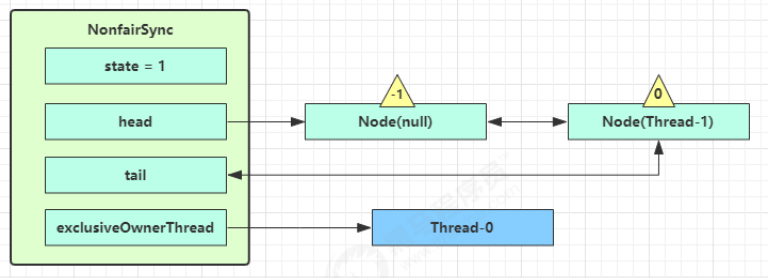
如果自己是紧邻着 head(排第二位),那么再次 tryAcquire 尝试获取锁,当然这时 state 仍为 1,失败
进入 shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire 逻辑,将前驱 node,即 head 的 waitStatus 改为 -1,表示有责任唤醒后继节点,这次返回 false
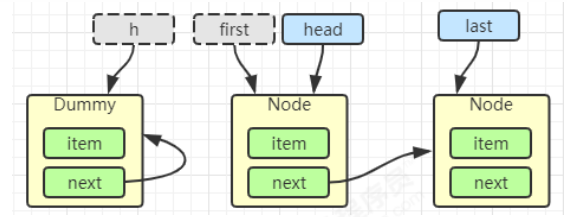
shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire 执行完毕回到 acquireQueued ,再次 tryAcquire 尝试获取锁,当然这时state 仍为 1,失败
当再次进入 shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire 时,这时因为其前驱 node 的 waitStatus 已经是 -1,这次返回true
进入 parkAndCheckInterrupt,Thread-1 park(灰色表示)
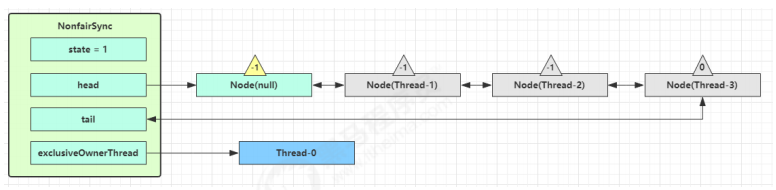
再次有多个线程经历上述过程竞争失败,变成这个样子
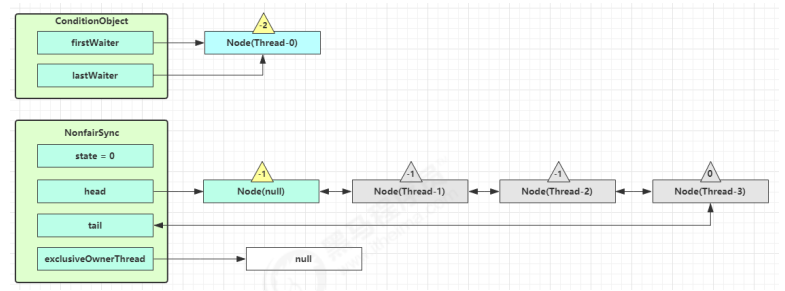
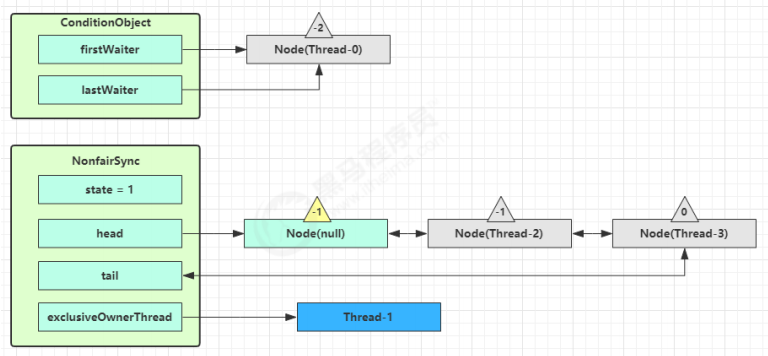
原 OwnerThread 释放锁时 1 2 3 public void unlock () { sync.release(1 ); }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public final boolean release (int arg) { if (tryRelease(arg)) { Node h = head; if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0 ) unparkSuccessor(h); return true ; } return false ; }
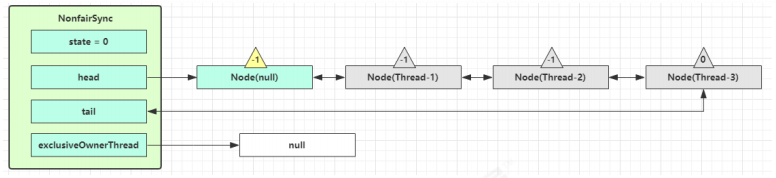
Thread-0 释放锁,进入 tryRelease 流程,如果成功
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 protected final boolean tryRelease (int releases) { int c = getState() - releases; if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread()) throw new IllegalMonitorStateException (); boolean free = false ; if (c == 0 ) { free = true ; setExclusiveOwnerThread(null ); } setState(c); return free; }
设置 exclusiveOwnerThread 为 null
state = 0
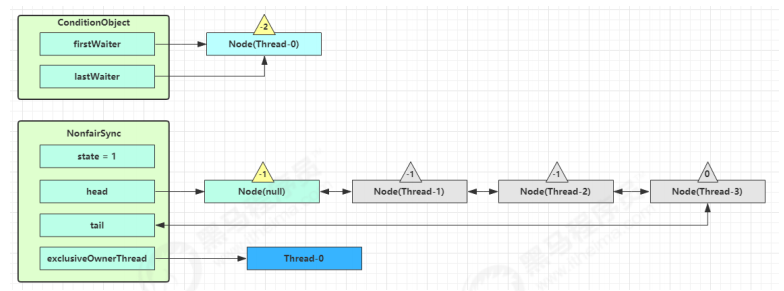
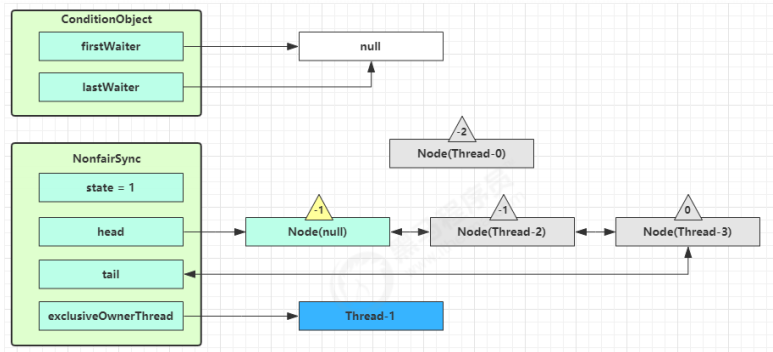
队列内线程抢到锁 当前队列不为 null,并且 head 的 waitStatus = -1,进入 unparkSuccessor 流程,唤醒下一个线程
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 private void unparkSuccessor (Node node) { int ws = node.waitStatus; if (ws < 0 ) compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0 ); Node s = node.next; if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0 ) { s = null ; for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev) if (t.waitStatus <= 0 ) s = t; } if (s != null ) LockSupport.unpark(s.thread); }
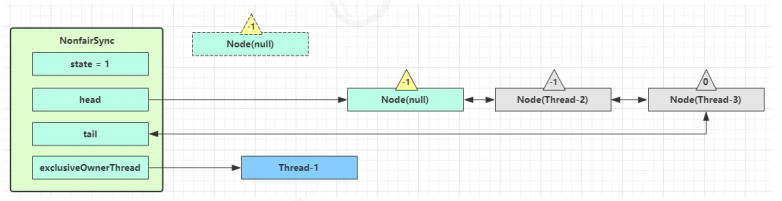
找到队列中离 head 最近的一个 Node(没取消的),unpark 恢复其运行,本例中即为 Thread-1
回到 Thread-1 的 acquireQueued 流程
如果加锁成功(没有竞争),会设置
exclusiveOwnerThread 为 Thread-1,state = 1
head 指向刚刚 Thread-1 所在的 Node,该 Node 清空 Thread
原本的 head 因为从链表断开,而可被垃圾回收
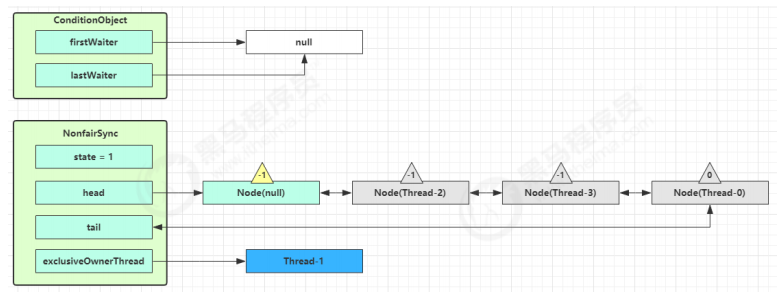
队列外线程抢到锁 如果这时候有其它线程来竞争(非公平的体现),例如这时有 Thread-4 来了
如果不巧又被 Thread-4 占了先
Thread-4 被设置为 exclusiveOwnerThread,state = 1
Thread-1 再次进入 acquireQueued 流程,获取锁失败,重新进入 park 阻塞
加锁源码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 static final class NonfairSync extends Sync { private static final long serialVersionUID = 7316153563782823691L ; final void lock () { if (compareAndSetState(0 , 1 )) setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread()); else acquire(1 ); } public final void acquire (int arg) { if ( !tryAcquire(arg) && acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg) ) { selfInterrupt(); } } protected final boolean tryAcquire (int acquires) { return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires); } final boolean nonfairTryAcquire (int acquires) { final Thread current = Thread.currentThread(); int c = getState(); if (c == 0 ) { if (compareAndSetState(0 , acquires)) { setExclusiveOwnerThread(current); return true ; } } else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) { int nextc = c + acquires; if (nextc < 0 ) throw new Error ("Maximum lock count exceeded" ); setState(nextc); return true ; } return false ; } private Node addWaiter (Node mode) { Node node = new Node (Thread.currentThread(), mode); Node pred = tail; if (pred != null ) { node.prev = pred; if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) { pred.next = node; return node; } } enq(node); return node; } private Node enq (final Node node) { for (;;) { Node t = tail; if (t == null ) { if (compareAndSetHead(new Node ())) { tail = head; } } else { node.prev = t; if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) { t.next = node; return t; } } } } final boolean acquireQueued (final Node node, int arg) { boolean failed = true ; try { boolean interrupted = false ; for (;;) { final Node p = node.predecessor(); if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) { setHead(node); p.next = null ; failed = false ; return interrupted; } if ( shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) && parkAndCheckInterrupt() ) { interrupted = true ; } } } finally { if (failed) cancelAcquire(node); } } private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire (Node pred, Node node) { int ws = pred.waitStatus; if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) { return true ; } if (ws > 0 ) { do { node.prev = pred = pred.prev; } while (pred.waitStatus > 0 ); pred.next = node; } else { compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL); } return false ; } private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt () { LockSupport.park(this ); return Thread.interrupted(); } }
注意
是否需要 unpark 是由当前节点的前驱节点的 waitStatus == Node.SIGNAL 来决定,而不是本节点的 waitStatus 决定
解锁源码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 static final class NonfairSync extends Sync { public void unlock () { sync.release(1 ); } public final boolean release (int arg) { if (tryRelease(arg)) { Node h = head; if ( h != null && h.waitStatus != 0 ) { unparkSuccessor(h); } return true ; } return false ; } protected final boolean tryRelease (int releases) { int c = getState() - releases; if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread()) throw new IllegalMonitorStateException (); boolean free = false ; if (c == 0 ) { free = true ; setExclusiveOwnerThread(null ); } setState(c); return free; } private void unparkSuccessor (Node node) { int ws = node.waitStatus; if (ws < 0 ) { compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0 ); } Node s = node.next; if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0 ) { s = null ; for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev) if (t.waitStatus <= 0 ) s = t; } if (s != null ) LockSupport.unpark(s.thread); } }
可重入原理 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 static final class NonfairSync extends Sync { final boolean nonfairTryAcquire (int acquires) { final Thread current = Thread.currentThread(); int c = getState(); if (c == 0 ) { if (compareAndSetState(0 , acquires)) { setExclusiveOwnerThread(current); return true ; } } else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) { int nextc = c + acquires; if (nextc < 0 ) throw new Error ("Maximum lock count exceeded" ); setState(nextc); return true ; } return false ; } protected final boolean tryRelease (int releases) { int c = getState() - releases; if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread()) throw new IllegalMonitorStateException (); boolean free = false ; if (c == 0 ) { free = true ; setExclusiveOwnerThread(null ); } setState(c); return free; } }
可打断原理 (默认)不可打断模式 在此模式下,即使它被打断,仍会驻留在 AQS 队列中,一直要等到获得锁后方能得知自己被打断了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 static final class NonfairSync extends Sync { private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt () { LockSupport.park(this ); return Thread.interrupted(); } final boolean acquireQueued (final Node node, int arg) { boolean failed = true ; try { boolean interrupted = false ; for (;;) { final Node p = node.predecessor(); if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) { setHead(node); p.next = null ; failed = false ; return interrupted; } if ( shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) && parkAndCheckInterrupt() ) { interrupted = true ; } } } finally { if (failed) cancelAcquire(node); } } public final void acquire (int arg) { if ( !tryAcquire(arg) && acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg) ) { selfInterrupt(); } } static void selfInterrupt () { Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); } }
可打断模式 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 static final class NonfairSync extends Sync { public final void acquireInterruptibly (int arg) throws InterruptedException { if (Thread.interrupted()) throw new InterruptedException (); if (!tryAcquire(arg)) doAcquireInterruptibly(arg); } private void doAcquireInterruptibly (int arg) throws InterruptedException { final Node node = addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE); boolean failed = true ; try { for (;;) { final Node p = node.predecessor(); if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) { setHead(node); p.next = null ; failed = false ; return ; } if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) && parkAndCheckInterrupt()) { throw new InterruptedException (); } } } finally { if (failed) cancelAcquire(node); } } }
公平锁实现原理 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 static final class FairSync extends Sync { private static final long serialVersionUID = -3000897897090466540L ; final void lock () { acquire(1 ); } public final void acquire (int arg) { if ( !tryAcquire(arg) && acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg) ) { selfInterrupt(); } } protected final boolean tryAcquire (int acquires) { final Thread current = Thread.currentThread(); int c = getState(); if (c == 0 ) { if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() && compareAndSetState(0 , acquires)) { setExclusiveOwnerThread(current); return true ; } } else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) { int nextc = c + acquires; if (nextc < 0 ) throw new Error ("Maximum lock count exceeded" ); setState(nextc); return true ; } return false ; } public final boolean hasQueuedPredecessors () { Node t = tail; Node h = head; Node s; return h != t && ( (s = h.next) == null || s.thread != Thread.currentThread() ); } }
条件变量实现原理 每个条件变量其实就对应着一个等待队列,其实现类是 ConditionObject
await 流程 开始 Thread-0 持有锁,调用 await,进入 ConditionObject 的 addConditionWaiter 流程
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public final void await () throws InterruptedException { if (Thread.interrupted()) throw new InterruptedException (); Node node = addConditionWaiter(); int savedState = fullyRelease(node); int interruptMode = 0 ; while (!isOnSyncQueue(node)) { LockSupport.park(this ); if ((interruptMode = checkInterruptWhileWaiting(node)) != 0 ) break ; } if (acquireQueued(node, savedState) && interruptMode != THROW_IE) interruptMode = REINTERRUPT; if (node.nextWaiter != null ) unlinkCancelledWaiters(); if (interruptMode != 0 ) reportInterruptAfterWait(interruptMode); }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 private Node addConditionWaiter () { Node t = lastWaiter; if (t != null && t.waitStatus != Node.CONDITION) { unlinkCancelledWaiters(); t = lastWaiter; } Node node = new Node (Thread.currentThread(), Node.CONDITION); if (t == null ) firstWaiter = node; else t.nextWaiter = node; lastWaiter = node; return node; }
创建新的 Node 状态为 -2(Node.CONDITION),关联 Thread-0,加入等待队列尾部
接下来进入 AQS 的 fullyRelease 流程,释放同步器上的锁
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 final int fullyRelease (Node node) { boolean failed = true ; try { int savedState = getState(); if (release(savedState)) { failed = false ; return savedState; } else { throw new IllegalMonitorStateException (); } } finally { if (failed) node.waitStatus = Node.CANCELLED; } }
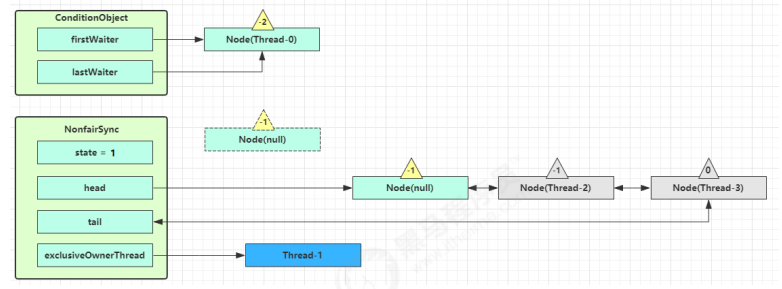
unpark AQS 队列中的下一个节点,竞争锁,假设没有其他竞争线程,那么 Thread-1 竞争成功
park 阻塞 Thread-0
signal 流程 假设 Thread-1 要来唤醒 Thread-0
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public final void signal () { if (!isHeldExclusively()) throw new IllegalMonitorStateException (); Node first = firstWaiter; if (first != null ) doSignal(first); }
进入 ConditionObject 的 doSignal 流程,取得等待队列中第一个 Node,即 Thread-0 所在 Node
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 private void doSignal (Node first) { do { if ( (firstWaiter = first.nextWaiter) == null ) lastWaiter = null ; first.nextWaiter = null ; } while (!transferForSignal(first) && (first = firstWaiter) != null ); }
执行 transferForSignal 流程,将该 Node 加入 AQS 队列尾部,将 Thread-0 的 waitStatus 改为 0,Thread-3 的waitStatus 改为 -1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 final boolean transferForSignal (Node node) { if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, Node.CONDITION, 0 )) return false ; Node p = enq(node); int ws = p.waitStatus; if (ws > 0 || !compareAndSetWaitStatus(p, ws, Node.SIGNAL)) LockSupport.unpark(node.thread); return true ; }
Thread-1 释放锁,进入 unlock 流程
源码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 public class ConditionObject implements Condition , java.io.Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1173984872572414699L ; private transient Node firstWaiter; private transient Node lastWaiter; public ConditionObject () { } private Node addConditionWaiter () { Node t = lastWaiter; if (t != null && t.waitStatus != Node.CONDITION) { unlinkCancelledWaiters(); t = lastWaiter; } Node node = new Node (Thread.currentThread(), Node.CONDITION); if (t == null ) firstWaiter = node; else t.nextWaiter = node; lastWaiter = node; return node; } private void doSignal (Node first) { do { if ( (firstWaiter = first.nextWaiter) == null ) { lastWaiter = null ; } first.nextWaiter = null ; } while ( !transferForSignal(first) && (first = firstWaiter) != null ); } final boolean transferForSignal (Node node) { if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, Node.CONDITION, 0 )) return false ; Node p = enq(node); int ws = p.waitStatus; if ( ws > 0 || !compareAndSetWaitStatus(p, ws, Node.SIGNAL) ) { LockSupport.unpark(node.thread); } return true ; } private void doSignalAll (Node first) { lastWaiter = firstWaiter = null ; do { Node next = first.nextWaiter; first.nextWaiter = null ; transferForSignal(first); first = next; } while (first != null ); } private void unlinkCancelledWaiters () { } public final void signal () { if (!isHeldExclusively()) throw new IllegalMonitorStateException (); Node first = firstWaiter; if (first != null ) doSignal(first); } public final void signalAll () { if (!isHeldExclusively()) throw new IllegalMonitorStateException (); Node first = firstWaiter; if (first != null ) doSignalAll(first); } public final void awaitUninterruptibly () { Node node = addConditionWaiter(); int savedState = fullyRelease(node); boolean interrupted = false ; while (!isOnSyncQueue(node)) { LockSupport.park(this ); if (Thread.interrupted()) interrupted = true ; } if (acquireQueued(node, savedState) || interrupted) selfInterrupt(); } final int fullyRelease (Node node) { boolean failed = true ; try { int savedState = getState(); if (release(savedState)) { failed = false ; return savedState; } else { throw new IllegalMonitorStateException (); } } finally { if (failed) node.waitStatus = Node.CANCELLED; } } private static final int REINTERRUPT = 1 ; private static final int THROW_IE = -1 ; private int checkInterruptWhileWaiting (Node node) { return Thread.interrupted() ? (transferAfterCancelledWait(node) ? THROW_IE : REINTERRUPT) : 0 ; } private void reportInterruptAfterWait (int interruptMode) throws InterruptedException { if (interruptMode == THROW_IE) throw new InterruptedException (); else if (interruptMode == REINTERRUPT) selfInterrupt(); } public final void await () throws InterruptedException { if (Thread.interrupted()) { throw new InterruptedException (); } Node node = addConditionWaiter(); int savedState = fullyRelease(node); int interruptMode = 0 ; while (!isOnSyncQueue(node)) { LockSupport.park(this ); if ((interruptMode = checkInterruptWhileWaiting(node)) != 0 ) break ; } if (acquireQueued(node, savedState) && interruptMode != THROW_IE) interruptMode = REINTERRUPT; if (node.nextWaiter != null ) unlinkCancelledWaiters(); if (interruptMode != 0 ) reportInterruptAfterWait(interruptMode); } public final long awaitNanos (long nanosTimeout) throws InterruptedException { if (Thread.interrupted()) { throw new InterruptedException (); } Node node = addConditionWaiter(); int savedState = fullyRelease(node); final long deadline = System.nanoTime() + nanosTimeout; int interruptMode = 0 ; while (!isOnSyncQueue(node)) { if (nanosTimeout <= 0L ) { transferAfterCancelledWait(node); break ; } if (nanosTimeout >= spinForTimeoutThreshold) LockSupport.parkNanos(this , nanosTimeout); if ((interruptMode = checkInterruptWhileWaiting(node)) != 0 ) break ; nanosTimeout = deadline - System.nanoTime(); } if (acquireQueued(node, savedState) && interruptMode != THROW_IE) interruptMode = REINTERRUPT; if (node.nextWaiter != null ) unlinkCancelledWaiters(); if (interruptMode != 0 ) reportInterruptAfterWait(interruptMode); return deadline - System.nanoTime(); } public final boolean awaitUntil (Date deadline) throws InterruptedException { } public final boolean await (long time, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException { } }
读写锁 ReentrantReadWriteLock 当读操作远远高于写操作时,这时候使用 读写锁 让 读-读 可以并发,提高性能。
类似于数据库中的 select ... from ... lock in share mode
示例 提供一个 数据容器类 内部分别使用读锁保护数据的 read() 方法,写锁保护数据的 write() 方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 class DataContainer { private Object data; private ReentrantReadWriteLock rw = new ReentrantReadWriteLock (); private ReentrantReadWriteLock.ReadLock r = rw.readLock(); private ReentrantReadWriteLock.WriteLock w = rw.writeLock(); public Object read () { log.debug("获取读锁..." ); r.lock(); try { log.debug("读取" ); sleep(1 ); return data; } finally { log.debug("释放读锁..." ); r.unlock(); } } public void write () { log.debug("获取写锁..." ); w.lock(); try { log.debug("写入" ); sleep(1 ); } finally { log.debug("释放写锁..." ); w.unlock(); } } }
读-读 可并发 测试 读锁-读锁 可以并发
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 DataContainer dataContainer = new DataContainer ();new Thread (() -> { dataContainer.read(); }, "t1" ).start(); new Thread (() -> { dataContainer.read(); }, "t2" ).start();
输出结果,从这里可以看到 Thread-0 锁定期间,Thread-1 的读操作不受影响
1 2 3 4 5 6 14 :05 :14.341 c.DataContainer [t2] - 获取读锁... 14 :05 :14.341 c.DataContainer [t1] - 获取读锁... 14 :05 :14.345 c.DataContainer [t1] - 读取14 :05 :14.345 c.DataContainer [t2] - 读取14 :05 :15.365 c.DataContainer [t2] - 释放读锁... 14 :05 :15.386 c.DataContainer [t1] - 释放读锁...
读-写 / 写-写 互斥 测试 读锁-写锁 相互阻塞
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 DataContainer dataContainer = new DataContainer ();new Thread (() -> { dataContainer.read(); }, "t1" ).start(); Thread.sleep(100 ); new Thread (() -> { dataContainer.write(); }, "t2" ).start();
输出结果
1 2 3 4 5 6 14 :04 :21.838 c.DataContainer [t1] - 获取读锁... 14 :04 :21.838 c.DataContainer [t2] - 获取写锁... 14 :04 :21.841 c.DataContainer [t2] - 写入14 :04 :22.843 c.DataContainer [t2] - 释放写锁... 14 :04 :22.843 c.DataContainer [t1] - 读取14 :04 :23.843 c.DataContainer [t1] - 释放读锁...
写锁-写锁 也是相互阻塞的,这里就不测试了
注意事项
读锁不支持条件变量,写锁支持
重入时不支持升级:即持有读锁的情况下去获取写锁,会导致获取写锁永久等待
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 r.lock(); try { w.lock(); try { } finally { w.unlock(); } } finally { r.unlock(); }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class CachedData { Object data; volatile boolean cacheValid; final ReentrantReadWriteLock rwl = new ReentrantReadWriteLock (); void processCachedData () { rwl.readLock().lock(); if (!cacheValid) { rwl.readLock().unlock(); rwl.writeLock().lock(); try { if (!cacheValid) { data = ... cacheValid = true ; } rwl.readLock().lock(); } finally { rwl.writeLock().unlock(); } } try { use(data); } finally { rwl.readLock().unlock(); } } }
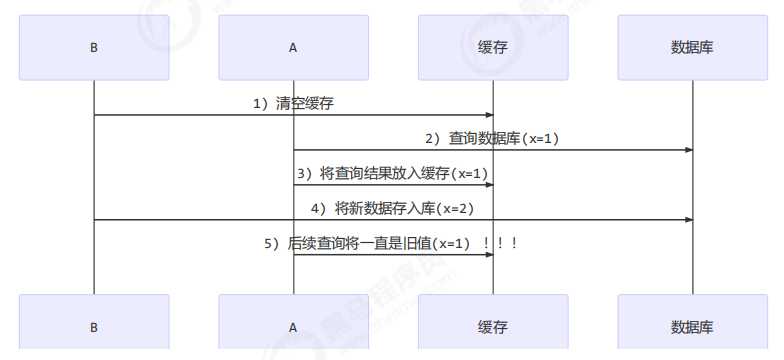
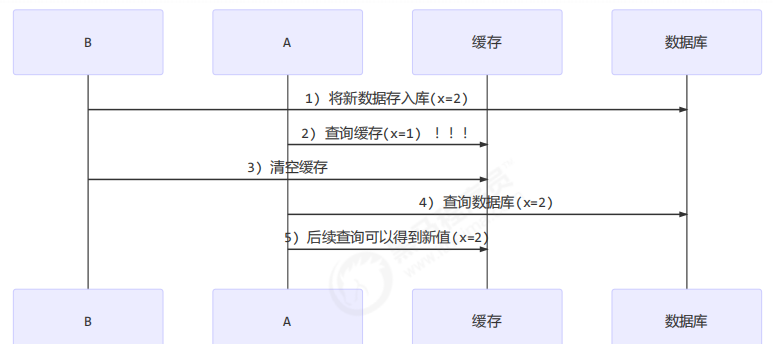
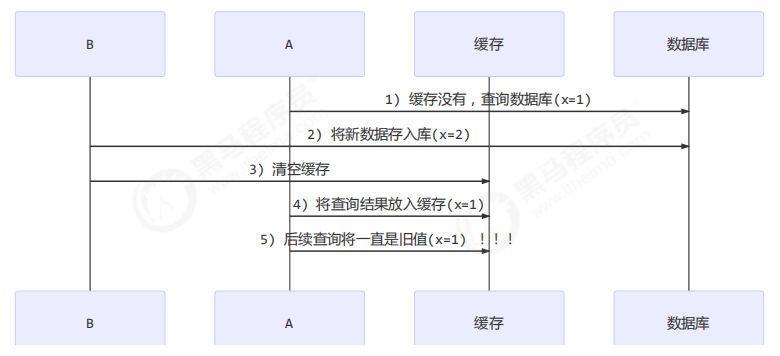
应用之缓存 缓存更新策略 更新时,是先清缓存还是先更新数据库
先清缓存
先更新数据库
补充一种情况,假设查询线程 A 查询数据时恰好缓存数据由于时间到期失效,或是第一次查询
这种情况的出现几率非常小,见 facebook 论文
读写锁实现一致性缓存 使用读写锁实现一个简单的按需加载缓存
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 class GenericCachedDao <T> { HashMap<SqlPair, T> map = new HashMap <>(); ReentrantReadWriteLock lock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock (); GenericDao genericDao = new GenericDao (); public int update (String sql, Object... params) { SqlPair key = new SqlPair (sql, params); lock.writeLock().lock(); try { int rows = genericDao.update(sql, params); map.clear(); return rows; } finally { lock.writeLock().unlock(); } } public T queryOne (Class<T> beanClass, String sql, Object... params) { SqlPair key = new SqlPair (sql, params); lock.readLock().lock(); try { T value = map.get(key); if (value != null ) { return value; } } finally { lock.readLock().unlock(); } lock.writeLock().lock(); try { T value = map.get(key); if (value == null ) { value = genericDao.queryOne(beanClass, sql, params); map.put(key, value); } return value; } finally { lock.writeLock().unlock(); } } class SqlPair { private String sql; private Object[] params; public SqlPair (String sql, Object[] params) { this .sql = sql; this .params = params; } @Override public boolean equals (Object o) { if (this == o) { return true ; } if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) { return false ; } SqlPair sqlPair = (SqlPair) o; return sql.equals(sqlPair.sql) && Arrays.equals(params, sqlPair.params); } @Override public int hashCode () { int result = Objects.hash(sql); result = 31 * result + Arrays.hashCode(params); return result; } } }
注意
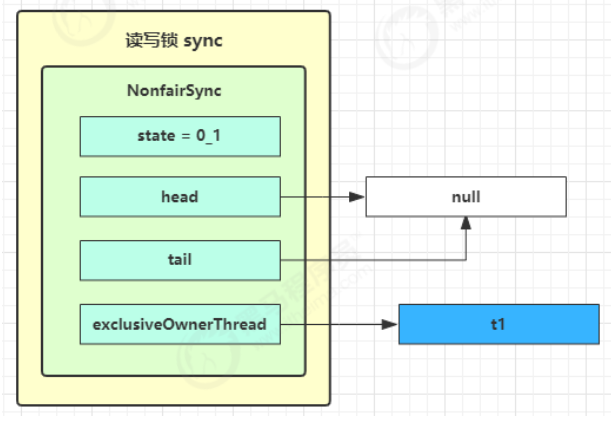
读写锁原理 图解流程 读写锁用的是同一个 Sycn 同步器,因此等待队列、state 等也是同一个
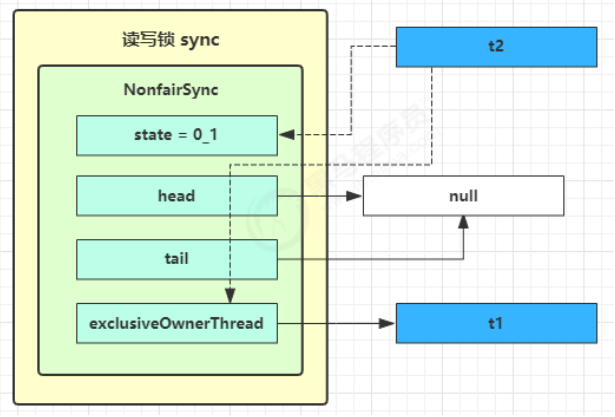
t1 w.lock,t2 r.lock 1) t1 成功上锁,流程与 ReentrantLock 加锁相比没有特殊之处,不同是写锁状态占了 state 的低 16 位,而读锁使用的是 state 的高 16 位
1 2 3 public void lock () { sync.acquire(1 ); }
1 2 3 4 public final void acquire (int arg) { if (!tryAcquire(arg) && acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg)) selfInterrupt(); }
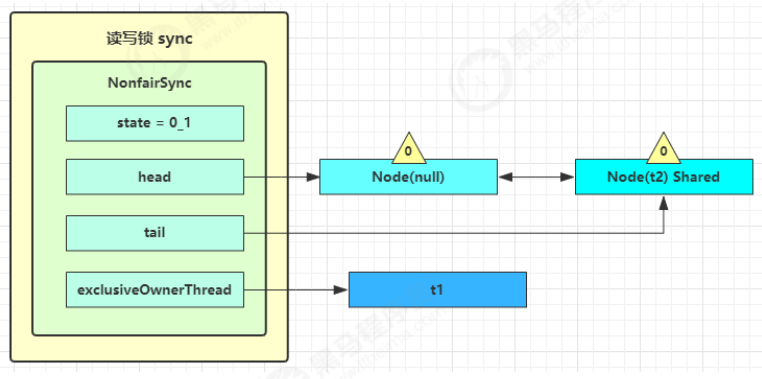
2)t2 执行 r.lock,这时进入读锁的 sync.acquireShared(1) 流程,首先会进入tryAcquireShared 流程。如果有写锁占据,那么 tryAcquireShared 返回 -1 表示失败
1 2 3 public void lock () { sync.acquireShared(1 ); }
1 2 3 4 public final void acquireShared (int arg) { if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0 ) doAcquireShared(arg); }
tryAcquireShared 返回值表示
-1 表示失败
0 表示成功,但后继节点不会继续唤醒
正数表示成功,而且数值是还有几个后继节点需要唤醒,读写锁返回 1
3)这时会进入 sync.doAcquireShared(1) 流程,首先也是调用 addWaiter 添加节点,不同之处在于节点被设置为Node.SHARED 模式而非 Node.EXCLUSIVE 模式,注意此时 t2 仍处于活跃状态
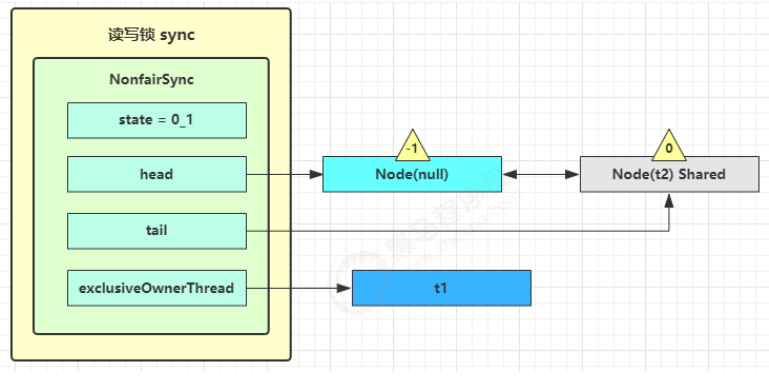
4)t2 会看看自己的节点是不是老二,如果是,还会再次调用 tryAcquireShared(1) 来尝试获取锁
5)如果没有成功,在 doAcquireShared 内 for (;;) 循环一次,把前驱节点的 waitStatus 改为 -1,再 for (;;) 循环一次尝试 tryAcquireShared(1) 如果还不成功,那么在 parkAndCheckInterrupt() 处 park
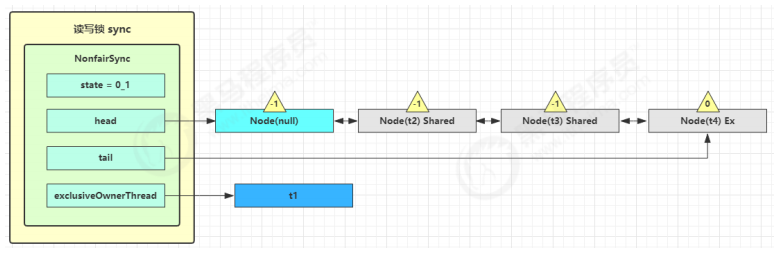
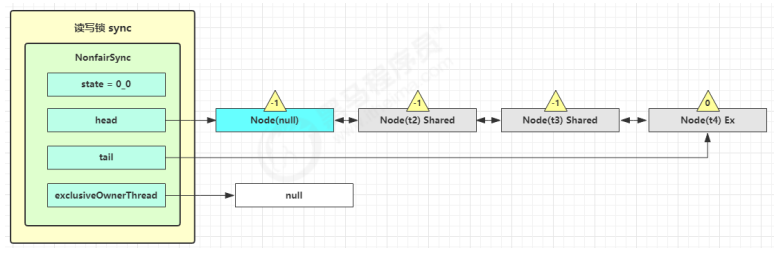
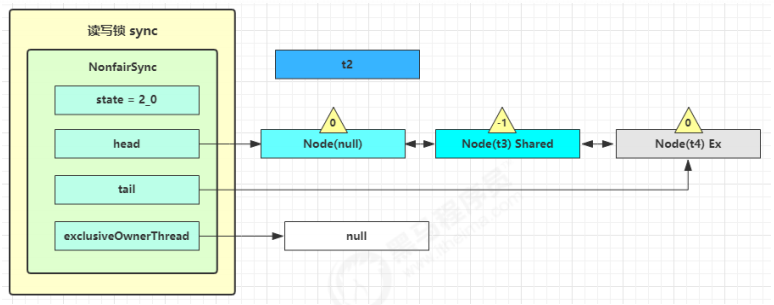
t3 r.lock,t4 w.lock 这种状态下,假设又有 t3 加读锁和 t4 加写锁,这期间 t1 仍然持有锁,就变成了下面的样子
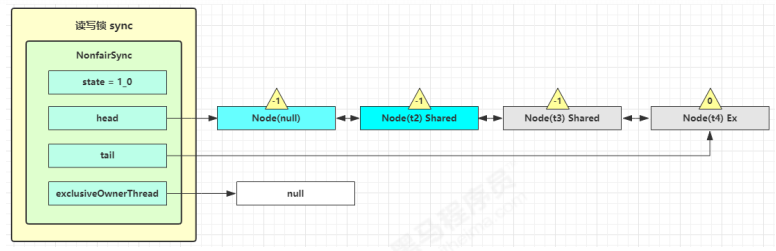
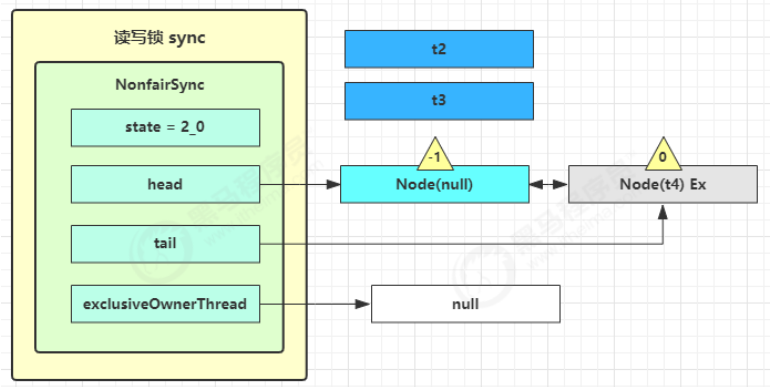
t1 w.unlock 这时会走到写锁的 sync.release(1) 流程,调用 sync.tryRelease(1) 成功,变成下面的样子
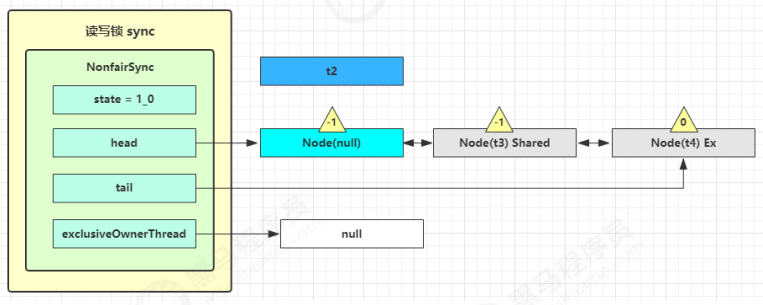
接下来执行唤醒流程 sync.unparkSuccessor,即让老二恢复运行,这时 t2 在 doAcquireShared 内parkAndCheckInterrupt() 处恢复运行
这回再来一次 for (;;) 执行 tryAcquireShared 成功则让读锁计数加一
这时 t2 已经恢复运行,接下来 t2 调用 setHeadAndPropagate(node, 1),它原本所在节点被置为头节点
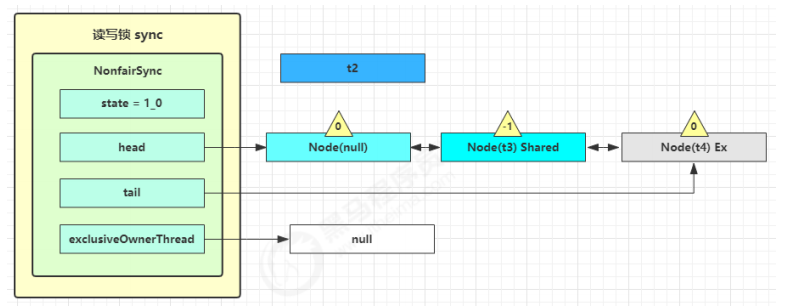
事情还没完,在 setHeadAndPropagate 方法内还会检查下一个节点是否是 shared,如果是则调用
doReleaseShared() 将 head 的状态从 -1 改为 0 并唤醒老二,这时 t3 在 doAcquireShared 内parkAndCheckInterrupt() 处恢复运行
这回再来一次 for (;;) 执行 tryAcquireShared 成功则让读锁计数加一
这时 t3 已经恢复运行,接下来 t3 调用 setHeadAndPropagate(node, 1),它原本所在节点被置为头节点
下一个节点不是 shared 了,因此不会继续唤醒 t4 所在节点
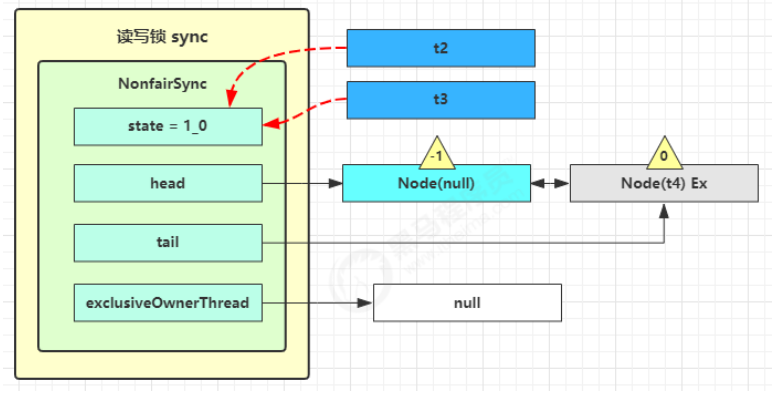
t2 r.unlock,t3 r.unlock t2 进入 sync.releaseShared(1) 中,调用 tryReleaseShared(1) 让计数减一,但由于计数还不为零
t3 进入 sync.releaseShared(1) 中,调用 tryReleaseShared(1) 让计数减一,这回计数为零了,进入
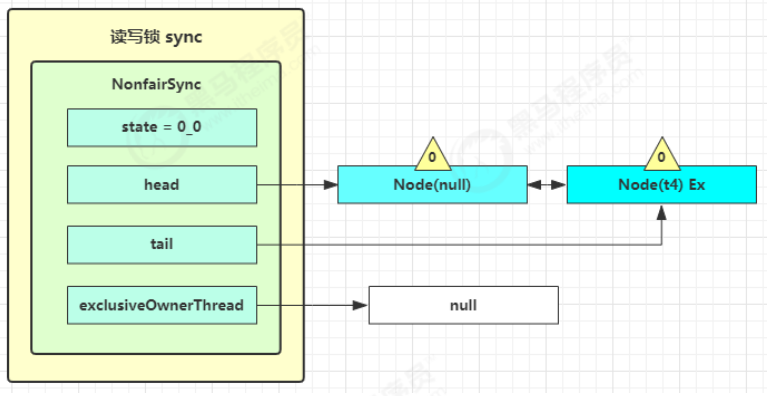
doReleaseShared() 将头节点从 -1 改为 0 并唤醒老二,即
之后 t4 在 acquireQueued 中 parkAndCheckInterrupt 处恢复运行,再次 for (;;) 这次自己是老二,并且没有其他竞争,tryAcquire(1) 成功,修改头结点,流程结束
源码分析 写锁上锁流程 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 static final class NonfairSync extends Sync { public void lock () { sync.acquire(1 ); } public final void acquire (int arg) { if ( !tryAcquire(arg) && acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg) ) { selfInterrupt(); } } protected final boolean tryAcquire (int acquires) { Thread current = Thread.currentThread(); int c = getState(); int w = exclusiveCount(c); if (c != 0 ) { if ( w == 0 || current != getExclusiveOwnerThread() ) { return false ; } if (w + exclusiveCount(acquires) > MAX_COUNT) throw new Error ("Maximum lock count exceeded" ); setState(c + acquires); return true ; } if ( writerShouldBlock() || !compareAndSetState(c, c + acquires) ) { return false ; } setExclusiveOwnerThread(current); return true ; } final boolean writerShouldBlock () { return false ; } }
写锁释放流程 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 static final class NonfairSync extends Sync { public void unlock () { sync.release(1 ); } public final boolean release (int arg) { if (tryRelease(arg)) { Node h = head; if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0 ) unparkSuccessor(h); return true ; } return false ; } protected final boolean tryRelease (int releases) { if (!isHeldExclusively()) throw new IllegalMonitorStateException (); int nextc = getState() - releases; boolean free = exclusiveCount(nextc) == 0 ; if (free) { setExclusiveOwnerThread(null ); } setState(nextc); return free; } }
读锁上锁流程 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 static final class NonfairSync extends Sync { public void lock () { sync.acquireShared(1 ); } public final void acquireShared (int arg) { if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0 ) { doAcquireShared(arg); } } protected final int tryAcquireShared (int unused) { Thread current = Thread.currentThread(); int c = getState(); if ( exclusiveCount(c) != 0 && getExclusiveOwnerThread() != current ) { return -1 ; } int r = sharedCount(c); if ( !readerShouldBlock() && r < MAX_COUNT && compareAndSetState(c, c + SHARED_UNIT) ) { return 1 ; } return fullTryAcquireShared(current); } final boolean readerShouldBlock () { return apparentlyFirstQueuedIsExclusive(); } final int fullTryAcquireShared (Thread current) { HoldCounter rh = null ; for (;;) { int c = getState(); if (exclusiveCount(c) != 0 ) { if (getExclusiveOwnerThread() != current) return -1 ; } else if (readerShouldBlock()) { } if (sharedCount(c) == MAX_COUNT) throw new Error ("Maximum lock count exceeded" ); if (compareAndSetState(c, c + SHARED_UNIT)) { return 1 ; } } } private void doAcquireShared (int arg) { final Node node = addWaiter(Node.SHARED); boolean failed = true ; try { boolean interrupted = false ; for (;;) { final Node p = node.predecessor(); if (p == head) { int r = tryAcquireShared(arg); if (r >= 0 ) { setHeadAndPropagate(node, r); p.next = null ; if (interrupted) selfInterrupt(); failed = false ; return ; } } if ( shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) && parkAndCheckInterrupt() ) { interrupted = true ; } } } finally { if (failed) cancelAcquire(node); } } private void setHeadAndPropagate (Node node, int propagate) { Node h = head; setHead(node); if (propagate > 0 || h == null || h.waitStatus < 0 || (h = head) == null || h.waitStatus < 0 ) { Node s = node.next; if (s == null || s.isShared()) { doReleaseShared(); } } } private void doReleaseShared () { for (;;) { Node h = head; if (h != null && h != tail) { int ws = h.waitStatus; if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) { if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, Node.SIGNAL, 0 )) continue ; unparkSuccessor(h); } else if (ws == 0 && !compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, 0 , Node.PROPAGATE)) continue ; } if (h == head) break ; } } }
读锁释放流程 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 static final class NonfairSync extends Sync { public void unlock () { sync.releaseShared(1 ); } public final boolean releaseShared (int arg) { if (tryReleaseShared(arg)) { doReleaseShared(); return true ; } return false ; } protected final boolean tryReleaseShared (int unused) { for (;;) { int c = getState(); int nextc = c - SHARED_UNIT; if (compareAndSetState(c, nextc)) { return nextc = = 0 ; } } } private void doReleaseShared () { for (;;) { Node h = head; if (h != null && h != tail) { int ws = h.waitStatus; if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) { if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, Node.SIGNAL, 0 )) continue ; unparkSuccessor(h); } else if (ws == 0 && !compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, 0 , Node.PROPAGATE)) continue ; } if (h == head) break ; } } }
StampedLock 使用读写锁时必须配合【戳】使用 该类自 JDK 8 加入,是为了进一步优化读性能,它的特点是在使用读锁、写锁时都必须配合【戳】使用
加解读锁
1 2 long stamp = lock.readLock();lock.unlockRead(stamp);
加解写锁
1 2 long stamp = lock.writeLock();lock.unlockWrite(stamp);
乐观读-锁升级 乐观读,StampedLock 支持 tryOptimisticRead() 方法(乐观读),读取完毕后需要做一次 戳校验 如果校验通过,表示这期间确实没有写操作,数据可以安全使用,如果校验没通过,需要重新获取读锁,保证数据安全。
1 2 3 4 5 long stamp = lock.tryOptimisticRead();if (!lock.validate(stamp)){ }
示例 提供一个 数据容器类 内部分别使用读锁保护数据的 read() 方法,写锁保护数据的 write() 方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 class DataContainerStamped { private int data; private final StampedLock lock = new StampedLock (); public DataContainerStamped (int data) { this .data = data; } public int read (int readTime) { long stamp = lock.tryOptimisticRead(); log.debug("optimistic read locking...{}" , stamp); sleep(readTime); if (lock.validate(stamp)) { log.debug("read finish...{}, data:{}" , stamp, data); return data; } log.debug("updating to read lock... {}" , stamp); try { stamp = lock.readLock(); log.debug("read lock {}" , stamp); sleep(readTime); log.debug("read finish...{}, data:{}" , stamp, data); return data; } finally { log.debug("read unlock {}" , stamp); lock.unlockRead(stamp); } } public void write (int newData) { long stamp = lock.writeLock(); log.debug("write lock {}" , stamp); try { sleep(2 ); this .data = newData; } finally { log.debug("write unlock {}" , stamp); lock.unlockWrite(stamp); } } }
测试 读-读 可以优化
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public static void main (String[] args) { DataContainerStamped dataContainer = new DataContainerStamped (1 ); new Thread (() -> { dataContainer.read(1 ); }, "t1" ).start(); sleep(0.5 ); new Thread (() -> { dataContainer.read(0 ); }, "t2" ).start(); }
输出结果,可以看到实际没有加读锁
1 2 3 4 15 :58 :50.217 c.DataContainerStamped [t1] - optimistic read locking...256 15 :58 :50.717 c.DataContainerStamped [t2] - optimistic read locking...256 15 :58 :50.717 c.DataContainerStamped [t2] - read finish...256 , data:1 15 :58 :51.220 c.DataContainerStamped [t1] - read finish...256 , data:1
测试 读-写 时优化读补加读锁
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public static void main (String[] args) { DataContainerStamped dataContainer = new DataContainerStamped (1 ); new Thread (() -> { dataContainer.read(1 ); }, "t1" ).start(); sleep(0.5 ); new Thread (() -> { dataContainer.write(100 ); }, "t2" ).start(); }
输出结果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 15 :57 :00.219 c.DataContainerStamped [t1] - optimistic read locking...256 15 :57 :00.717 c.DataContainerStamped [t2] - write lock 384 15 :57 :01.225 c.DataContainerStamped [t1] - updating to read lock... 256 15 :57 :02.719 c.DataContainerStamped [t2] - write unlock 384 15 :57 :02.719 c.DataContainerStamped [t1] - read lock 513 15 :57 :03.719 c.DataContainerStamped [t1] - read finish...513 , data:1000 15 :57 :03.719 c.DataContainerStamped [t1] - read unlock 513
注意
StampedLock 不支持条件变量
StampedLock 不支持锁重入
Semaphore 基本使用 信号量,用来限制能同时访问共享资源的线程上限。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public static void main (String[] args) { Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore (3 ); for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) { new Thread (() -> { try { semaphore.acquire(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { log.debug("running..." ); sleep(1 ); log.debug("end..." ); } finally { semaphore.release(); } }).start(); } }
输出
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 07 :35 :15.485 c.TestSemaphore [Thread-2 ] - running... 07 :35 :15.485 c.TestSemaphore [Thread-1 ] - running... 07 :35 :15.485 c.TestSemaphore [Thread-0 ] - running... 07 :35 :16.490 c.TestSemaphore [Thread-2 ] - end... 07 :35 :16.490 c.TestSemaphore [Thread-0 ] - end... 07 :35 :16.490 c.TestSemaphore [Thread-1 ] - end... 07 :35 :16.490 c.TestSemaphore [Thread-3 ] - running... 07 :35 :16.490 c.TestSemaphore [Thread-5 ] - running... 07 :35 :16.490 c.TestSemaphore [Thread-4 ] - running... 07 :35 :17.490 c.TestSemaphore [Thread-5 ] - end... 07 :35 :17.490 c.TestSemaphore [Thread-4 ] - end... 07 :35 :17.490 c.TestSemaphore [Thread-3 ] - end... 07 :35 :17.490 c.TestSemaphore [Thread-6 ] - running... 07 :35 :17.490 c.TestSemaphore [Thread-7 ] - running... 07 :35 :17.490 c.TestSemaphore [Thread-9 ] - running... 07 :35 :18.491 c.TestSemaphore [Thread-6 ] - end... 07 :35 :18.491 c.TestSemaphore [Thread-7 ] - end... 07 :35 :18.491 c.TestSemaphore [Thread-9 ] - end... 07 :35 :18.491 c.TestSemaphore [Thread-8 ] - running... 07 :35 :19.492 c.TestSemaphore [Thread-8 ] - end...
Semaphore 应用 (实现简单连接池)
使用 Semaphore 限流,在访问高峰期时,让请求线程阻塞,高峰期过去再释放许可,当然它只适合限制单机线程数量,并且仅是限制线程数,而不是限制资源数(例如连接数,请对比 Tomcat LimitLatch 的实现)
用 Semaphore 实现简单连接池,对比『享元模式』下的实现(用wait notify),性能和可读性显然更好,注意下面的实现中线程数和数据库连接数是相等的
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 @Slf4j(topic = "c.Pool") class Pool { private final int poolSize; private Connection[] connections; private AtomicIntegerArray states; private Semaphore semaphore; public Pool (int poolSize) { this .poolSize = poolSize; this .semaphore = new Semaphore (poolSize); this .connections = new Connection [poolSize]; this .states = new AtomicIntegerArray (new int [poolSize]); for (int i = 0 ; i < poolSize; i++) { connections[i] = new MockConnection ("连接" + (i+1 )); } } public Connection borrow () { try { semaphore.acquire(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } for (int i = 0 ; i < poolSize; i++) { if (states.get(i) == 0 ) { if (states.compareAndSet(i, 0 , 1 )) { log.debug("borrow {}" , connections[i]); return connections[i]; } } } return null ; } public void free (Connection conn) { for (int i = 0 ; i < poolSize; i++) { if (connections[i] == conn) { states.set(i, 0 ); log.debug("free {}" , conn); semaphore.release(); break ; } } } }
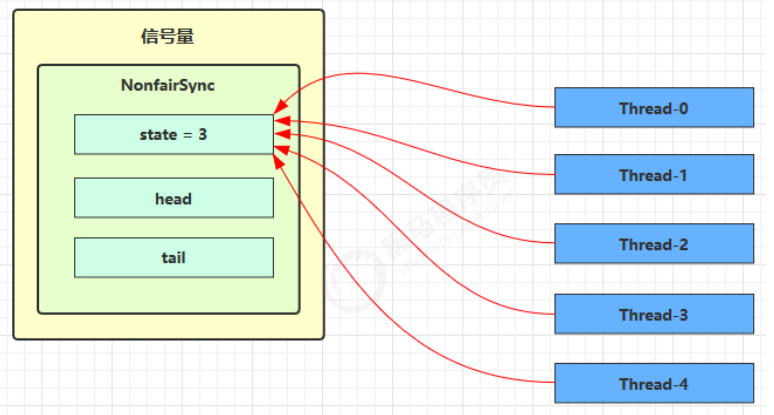
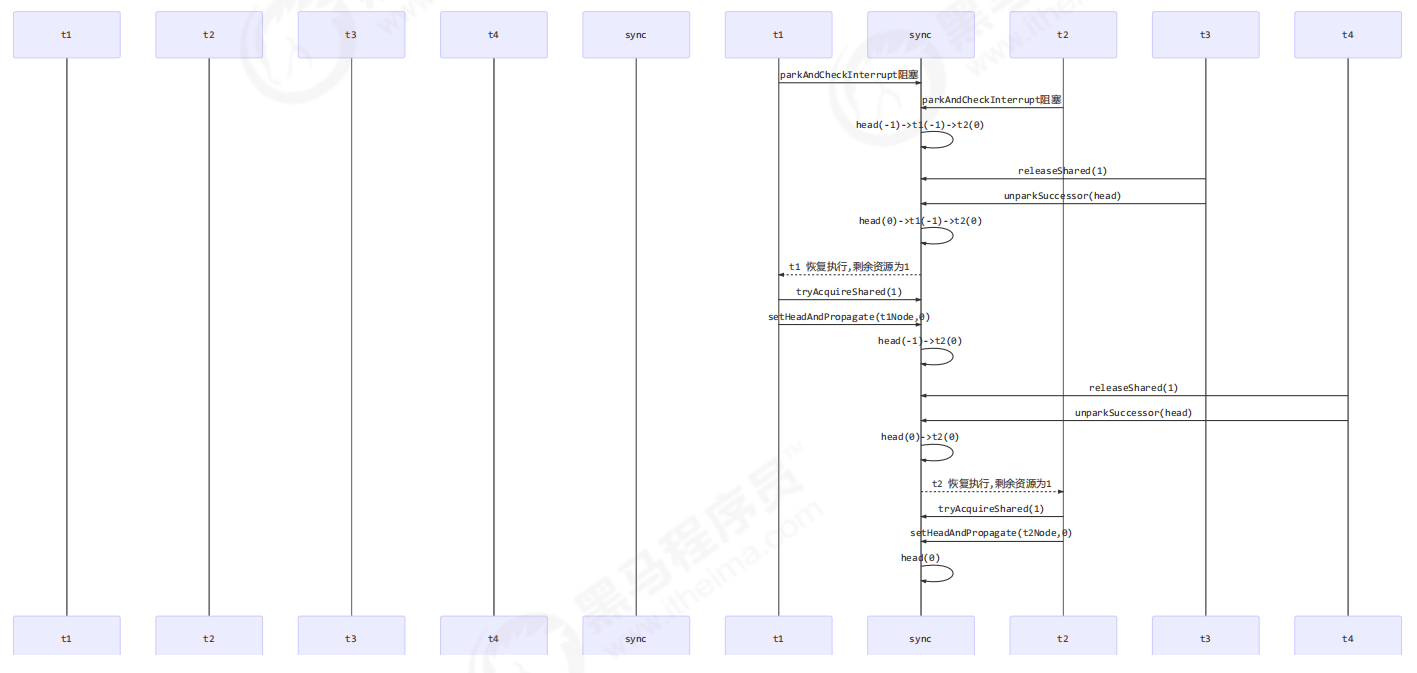
Semaphore 原理 加锁解锁流程 Semaphore 有点像一个停车场,permits 就好像停车位数量,当线程获得了 permits 就像是获得了停车位,然后停车场显示空余车位减一 ,刚开始,permits(state)为 3,这时 5 个线程来获取资源
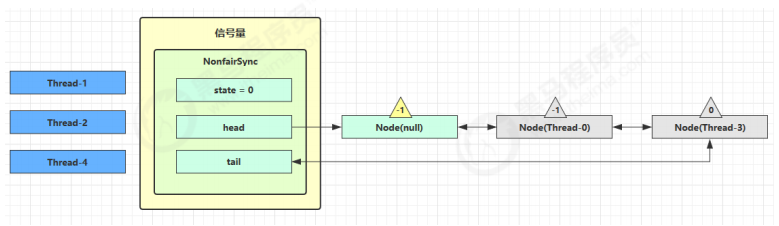
假设其中 Thread-1,Thread-2,Thread-4 cas 竞争成功,而 Thread-0 和 Thread-3 竞争失败,进入 AQS 队列 park 阻塞
这时 Thread-4 释放了 permits,状态如下
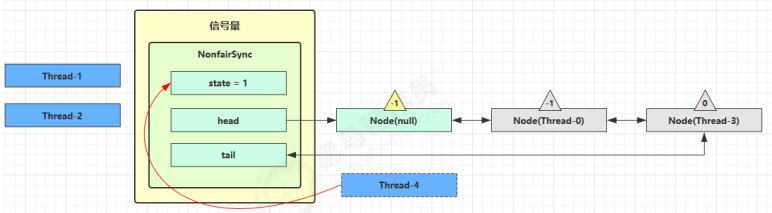
接下来 Thread-0 竞争成功,permits 再次设置为 0,设置自己为 head 节点,断开原来的 head 节点,unpark 接下来的 Thread-3 节点,但由于 permits 是 0,因此 Thread-3 在尝试不成功后再次进入 park 状态
源码分析 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 static final class NonfairSync extends Sync { private static final long serialVersionUID = -2694183684443567898L ; NonfairSync(int permits) { super (permits); } public void acquire () throws InterruptedException { sync.acquireSharedInterruptibly(1 ); } public final void acquireSharedInterruptibly (int arg) throws InterruptedException { if (Thread.interrupted()) throw new InterruptedException (); if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0 ) doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(arg); } protected int tryAcquireShared (int acquires) { return nonfairTryAcquireShared(acquires); } final int nonfairTryAcquireShared (int acquires) { for (;;) { int available = getState(); int remaining = available - acquires; if ( remaining < 0 || compareAndSetState(available, remaining) ) { return remaining; } } } private void doAcquireSharedInterruptibly (int arg) throws InterruptedException { final Node node = addWaiter(Node.SHARED); boolean failed = true ; try { for (;;) { final Node p = node.predecessor(); if (p == head) { int r = tryAcquireShared(arg); if (r >= 0 ) { setHeadAndPropagate(node, r); p.next = null ; failed = false ; return ; } } if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) && parkAndCheckInterrupt()) throw new InterruptedException (); } } finally { if (failed) cancelAcquire(node); } } public void release () { sync.releaseShared(1 ); } public final boolean releaseShared (int arg) { if (tryReleaseShared(arg)) { doReleaseShared(); return true ; } return false ; } protected final boolean tryReleaseShared (int releases) { for (;;) { int current = getState(); int next = current + releases; if (next < current) throw new Error ("Maximum permit count exceeded" ); if (compareAndSetState(current, next)) return true ; } } }
为什么要有 PROPAGATE 早期有 bug
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public final boolean releaseShared (int arg) { if (tryReleaseShared(arg)) { Node h = head; if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0 ) unparkSuccessor(h); return true ; } return false ; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 private void doAcquireShared (int arg) { final Node node = addWaiter(Node.SHARED); boolean failed = true ; try { boolean interrupted = false ; for (;;) { final Node p = node.predecessor(); if (p == head) { int r = tryAcquireShared(arg); if (r >= 0 ) { setHeadAndPropagate(node, r); p.next = null ; if (interrupted) selfInterrupt(); failed = false ; return ; } } if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) && parkAndCheckInterrupt()) interrupted = true ; } } finally { if (failed) cancelAcquire(node); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 private void setHeadAndPropagate (Node node, int propagate) { setHead(node); if (propagate > 0 && node.waitStatus != 0 ) { Node s = node.next; if (s == null || s.isShared()) unparkSuccessor(node); } }
假设存在某次循环中队列里排队的结点情况为head(-1)->t1(-1)->t2(-1)
假设存在将要信号量释放的 T3 和 T4,释放顺序为先 T3 后 T4
正常流程
产生bug的情况
修复前版本执行流程
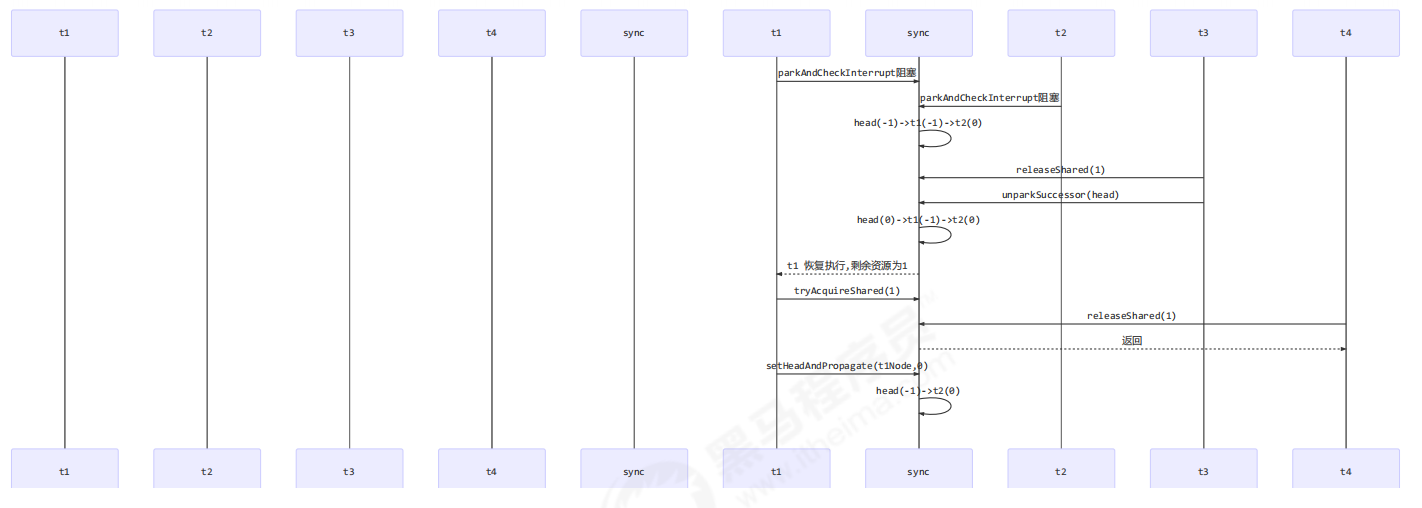
T3 调用 releaseShared(1),直接调用了 unparkSuccessor(head),head 的等待状态从 -1 变为 0
T1 由于 T3 释放信号量被唤醒,调用 tryAcquireShared,假设返回值为 0(获取锁成功,但没有剩余资源 量)
T4 调用 releaseShared(1),此时 head.waitStatus 为 0(此时读到的 head 和 1 中为同一个head),不满足条件,因此不调用 unparkSuccessor(head)
T1 获取信号量成功,调用 setHeadAndPropagate 时,因为不满足 propagate > 0(2 的返回值也就是propagate(剩余资源量) == 0),从而不会唤醒后继结点, T2 线程得不到唤醒
bug 修复后 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 private void setHeadAndPropagate (Node node, int propagate) { Node h = head; setHead(node); if (propagate > 0 || h == null || h.waitStatus < 0 || (h = head) == null || h.waitStatus < 0 ) { Node s = node.next; if (s == null || s.isShared()) { doReleaseShared(); } } } private void doReleaseShared () { for (;;) { Node h = head; if (h != null && h != tail) { int ws = h.waitStatus; if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) { if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, Node.SIGNAL, 0 )) continue ; unparkSuccessor(h); } else if (ws == 0 && !compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, 0 , Node.PROPAGATE)) continue ; } if (h == head) break ; } }
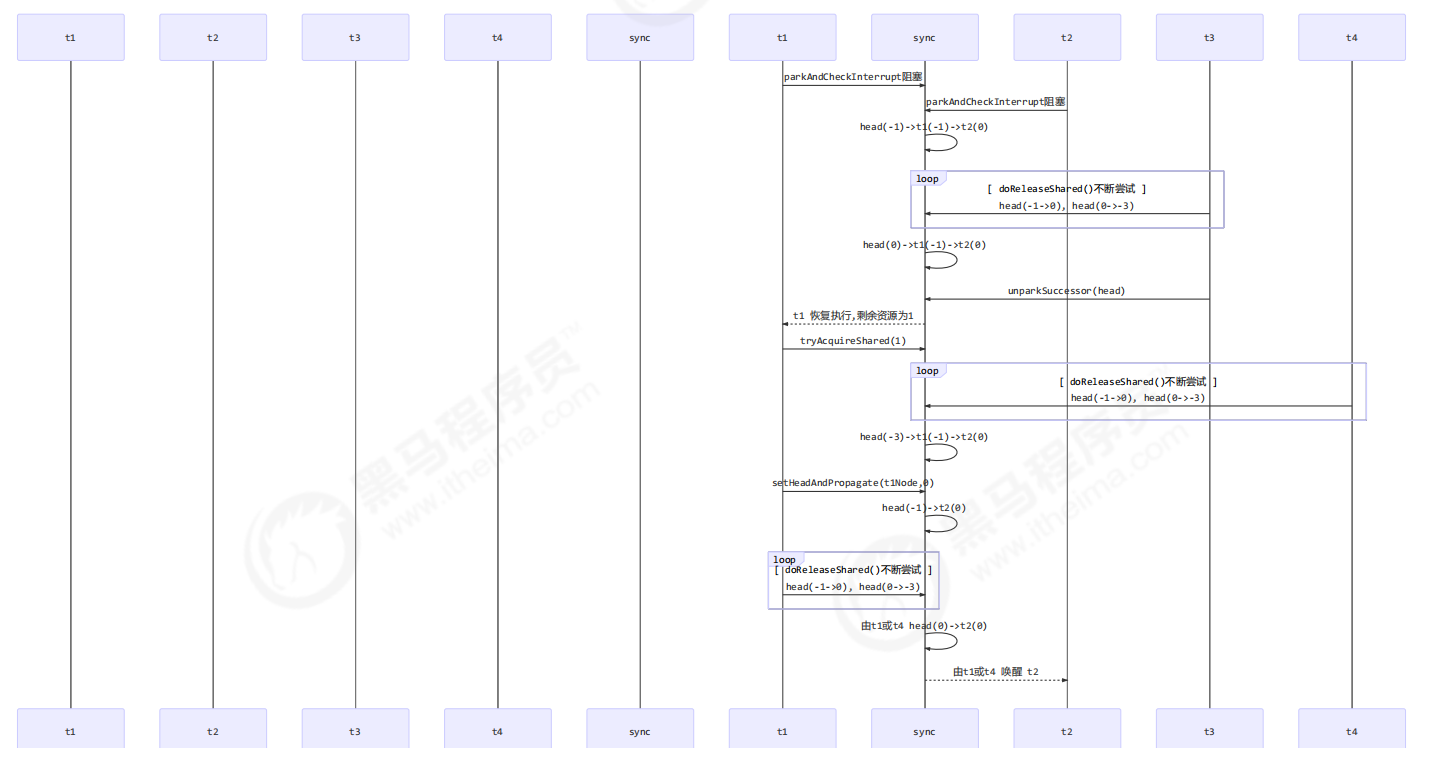
T3 调用 releaseShared(),直接调用了 unparkSuccessor(head),head 的等待状态从 -1 变为 0
T1 由于 T3 释放信号量被唤醒,调用 tryAcquireShared,假设返回值为 0(获取锁成功,但没有剩余资源量)
T4 调用 releaseShared(),此时 head.waitStatus 为 0(此时读到的 head 和 1 中为同一个 head),调用 doReleaseShared() 将等待状态置为 PROPAGATE(-3)
T1 获取信号量成功,调用 setHeadAndPropagate 时,读到 h.waitStatus < 0,从而调用 doReleaseShared() 唤醒 T2
CountdownLatch 倒计时锁:用来进行线程同步协作,等待所有线程完成倒计时。
其中构造参数用来初始化等待计数值,await() 用来等待计数归零,countDown() 用来让计数减一
示例1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 public static void main (String[] args) throws InterruptedException { CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch (3 ); new Thread (() -> { log.debug("begin..." ); sleep(1 ); latch.countDown(); log.debug("end...{}" , latch.getCount()); }).start(); new Thread (() -> { log.debug("begin..." ); sleep(2 ); latch.countDown(); log.debug("end...{}" , latch.getCount()); }).start(); new Thread (() -> { log.debug("begin..." ); sleep(1.5 ); latch.countDown(); log.debug("end...{}" , latch.getCount()); }).start(); log.debug("waiting..." ); latch.await(); log.debug("wait end..." ); }
输出
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 18 :44 :00.778 c.TestCountDownLatch [main] - waiting... 18 :44 :00.778 c.TestCountDownLatch [Thread-2 ] - begin... 18 :44 :00.778 c.TestCountDownLatch [Thread-0 ] - begin... 18 :44 :00.778 c.TestCountDownLatch [Thread-1 ] - begin... 18 :44 :01.782 c.TestCountDownLatch [Thread-0 ] - end...2 18 :44 :02.283 c.TestCountDownLatch [Thread-2 ] - end...1 18 :44 :02.782 c.TestCountDownLatch [Thread-1 ] - end...0 18 :44 :02.782 c.TestCountDownLatch [main] - wait end...
可以配合线程池使用,改进如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 public static void main (String[] args) throws InterruptedException { CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch (3 ); ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4 ); service.submit(() -> { log.debug("begin..." ); sleep(1 ); latch.countDown(); log.debug("end...{}" , latch.getCount()); }); service.submit(() -> { log.debug("begin..." ); sleep(1.5 ); latch.countDown(); log.debug("end...{}" , latch.getCount()); }); service.submit(() -> { log.debug("begin..." ); sleep(2 ); latch.countDown(); log.debug("end...{}" , latch.getCount()); }); service.submit(()->{ try { log.debug("waiting..." ); latch.await(); log.debug("wait end..." ); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); }
输出
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 18 :52 :25.831 c.TestCountDownLatch [pool-1 -thread-3 ] - begin... 18 :52 :25.831 c.TestCountDownLatch [pool-1 -thread-1 ] - begin... 18 :52 :25.831 c.TestCountDownLatch [pool-1 -thread-2 ] - begin... 18 :52 :25.831 c.TestCountDownLatch [pool-1 -thread-4 ] - waiting... 18 :52 :26.835 c.TestCountDownLatch [pool-1 -thread-1 ] - end...2 18 :52 :27.335 c.TestCountDownLatch [pool-1 -thread-2 ] - end...1 18 :52 :27.835 c.TestCountDownLatch [pool-1 -thread-3 ] - end...0 18 :52 :27.835 c.TestCountDownLatch [pool-1 -thread-4 ] - wait end...
应用之同步等待多线程准备完毕 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 AtomicInteger num = new AtomicInteger (0 );ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10 , (r) -> { return new Thread (r, "t" + num.getAndIncrement()); }); CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch (10 );String[] all = new String [10 ]; Random r = new Random ();for (int j = 0 ; j < 10 ; j++) { int x = j; service.submit(() -> { for (int i = 0 ; i <= 100 ; i++) { try { Thread.sleep(r.nextInt(100 )); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } all[x] = Thread.currentThread().getName() + "(" + (i + "%" ) + ")" ; System.out.print("\r" + Arrays.toString(all)); } latch.countDown(); }); } latch.await(); System.out.println("\n游戏开始..." ); service.shutdown();
中间输出
1 [t0(52%), t1(47%), t2(51%), t3(40%), t4(49%), t5(44%), t6(49%), t7(52%), t8(46%), t9(46%)]
最后输出
1 2 [t0(100%), t1(100%), t2(100%), t3(100%), t4(100%), t5(100%), t6(100%), t7(100%), t8(100%), t9(100%)] 游戏开始...
应用之同步等待多个远程调用结束 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 @RestController public class TestCountDownlatchController { @GetMapping("/order/{id}") public Map<String, Object> order (@PathVariable int id) { HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap <>(); map.put("id" , id); map.put("total" , "2300.00" ); sleep(2000 ); return map; } @GetMapping("/product/{id}") public Map<String, Object> product (@PathVariable int id) { HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap <>(); if (id == 1 ) { map.put("name" , "小爱音箱" ); map.put("price" , 300 ); } else if (id == 2 ) { map.put("name" , "小米手机" ); map.put("price" , 2000 ); } map.put("id" , id); sleep(1000 ); return map; } @GetMapping("/logistics/{id}") public Map<String, Object> logistics (@PathVariable int id) { HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap <>(); map.put("id" , id); map.put("name" , "中通快递" ); sleep(2500 ); return map; } private void sleep (int millis) { try { Thread.sleep(millis); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
rest 远程调用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate ();log.debug("begin" ); ExecutorService service = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch (4 );Future<Map<String,Object>> f1 = service.submit(() -> { Map<String, Object> r = restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:8080/order/{1}" , Map.class, 1 ); return r; }); Future<Map<String, Object>> f2 = service.submit(() -> { Map<String, Object> r = restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:8080/product/{1}" , Map.class, 1 ); return r; }); Future<Map<String, Object>> f3 = service.submit(() -> { Map<String, Object> r = restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:8080/product/{1}" , Map.class, 2 ); return r; }); Future<Map<String, Object>> f4 = service.submit(() -> { Map<String, Object> r = restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:8080/logistics/{1}" , Map.class, 1 ); return r; }); System.out.println(f1.get()); System.out.println(f2.get()); System.out.println(f3.get()); System.out.println(f4.get()); log.debug("执行完毕" ); service.shutdown();
执行结果
1 2 3 4 5 6 19 :51 :39.711 c.TestCountDownLatch [main] - begin {total=2300.00 , id=1 } {price=300 , name=小爱音箱, id=1 } {price=2000 , name=小米手机, id=2 } {name=中通快递, id=1 } 19 :51 :42.407 c.TestCountDownLatch [main] - 执行完毕
CyclicBarrier 循环栅栏,用来进行线程协作,等待线程满足某个计数。构造时设置『计数个数』,每个线程执行到某个需要“同步”的时刻调用 await() 方法进行等待,当等待的线程数满足『计数个数』时,继续执行.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 CyclicBarrier cb = new CyclicBarrier (2 ); new Thread (()->{ System.out.println("线程1开始.." +new Date ()); try { cb.await(); } catch (InterruptedException | BrokenBarrierException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("线程1继续向下运行..." +new Date ()); }).start(); new Thread (()->{ System.out.println("线程2开始.." +new Date ()); try { Thread.sleep(2000 ); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } try { cb.await(); } catch (InterruptedException | BrokenBarrierException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("线程2继续向下运行..." +new Date ()); }).start();
注意 CyclicBarrier 与 CountDownLatch 的主要区别在于 CyclicBarrier 是可以重用的 CyclicBarrier 可以被比喻为『人满发车』
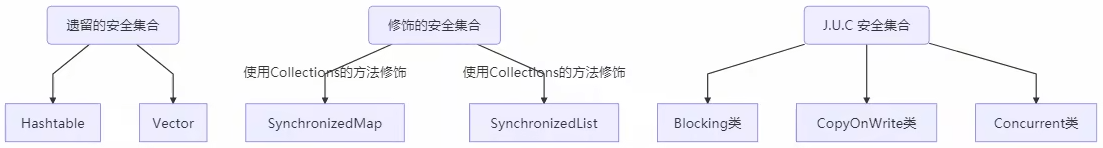
线程安全集合类概述
线程安全集合类可以分为三大类:
遗留的线程安全集合
遗留的线程安全集合如 Hashtable ,Vector
使用 Collections 装饰的线程安全集合
Collections.synchronizedCollection
Collections.synchronizedList
Collections.synchronizedMap
Collections.synchronizedSet
Collections.synchronizedNavigableMap
Collections.synchronizedNavigableSet
Collections.synchronizedSortedMap
Collections.synchronizedSortedSet
JUC下的安全集合: Blocking、CopyOnWrite、Concurrent 重点介绍 java.util.concurrent.* 下的线程安全集合类,可以发现它们有规律,里面包含三类关键词: Blocking、CopyOnWrite、Concurrent
遍历时如果发生了修改,对于非安全容器来讲,使用 fail-fast 机制也就是让遍历立刻失败,抛出ConcurrentModifificationException,不再继续遍历
ConcurrentHashMap 练习:单词计数 生成测试数据
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 static final String ALPHA = "abcedfghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz" ;public static void main (String[] args) { int length = ALPHA.length(); int count = 200 ; List<String> list = new ArrayList <>(length * count); for (int i = 0 ; i < length; i++) { char ch = ALPHA.charAt(i); for (int j = 0 ; j < count; j++) { list.add(String.valueOf(ch)); } } Collections.shuffle(list); for (int i = 0 ; i < 26 ; i++) { try (PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter ( new OutputStreamWriter ( new FileOutputStream ("tmp/" + (i+1 ) + ".txt" )))) { String collect = list.subList(i * count, (i + 1 ) * count).stream() .collect(Collectors.joining("\n" )); out.print(collect); } catch (IOException e) { } } }
模版代码,模版代码中封装了多线程读取文件的代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 private static <V> void demo (Supplier<Map<String,V>> supplier, BiConsumer<Map<String,V>,List<String>> consumer) { Map<String, V> counterMap = supplier.get(); List<Thread> ts = new ArrayList <>(); for (int i = 1 ; i <= 26 ; i++) { int idx = i; Thread thread = new Thread (() -> { List<String> words = readFromFile(idx); consumer.accept(counterMap, words); }); ts.add(thread); } ts.forEach(t->t.start()); ts.forEach(t-> { try { t.join(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); System.out.println(counterMap); } public static List<String> readFromFile (int i) { ArrayList<String> words = new ArrayList <>(); try (BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader (new InputStreamReader ( new FileInputStream ("tmp/" + i +".txt" )))) { while (true ) { String word = in.readLine(); if (word == null ) { break ; } words.add(word); } return words; } catch (IOException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } }
你要做的是实现两个参数
一是提供一个 map 集合,用来存放每个单词的计数结果,key 为单词,value 为计数
二是提供一组操作,保证计数的安全性,会传递 map 集合以及 单词 List
正确结果输出应该是每个单词出现 200 次
1 {a=200, b=200, c=200, d=200, e=200, f=200, g=200, h=200, i=200, j=200, k=200, l=200, m=200, n=200, o=200, p=200, q=200, r=200, s=200, t=200, u=200, v=200, w=200, x=200, y=200, z=200}
下面的实现为: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 demo( () -> new HashMap <String, Integer>(), (map, words) -> { for (String word : words) { Integer counter = map.get(word); int newValue = counter == null ? 1 : counter + 1 ; map.put(word, newValue); } } );
有没有问题?请改进
参考解答1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 demo( () -> new ConcurrentHashMap <String, LongAdder>(8 ,0.75f ,8 ), (map, words) -> { for (String word : words) { LongAdder value = map.computeIfAbsent(word, (key) -> new LongAdder ()); value.increment(); } } )
参考解答2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 demo( () -> new ConcurrentHashMap <String, Integer>(), (map, words) -> { for (String word : words) { map.merge(word, 1 , Integer::sum); } } );
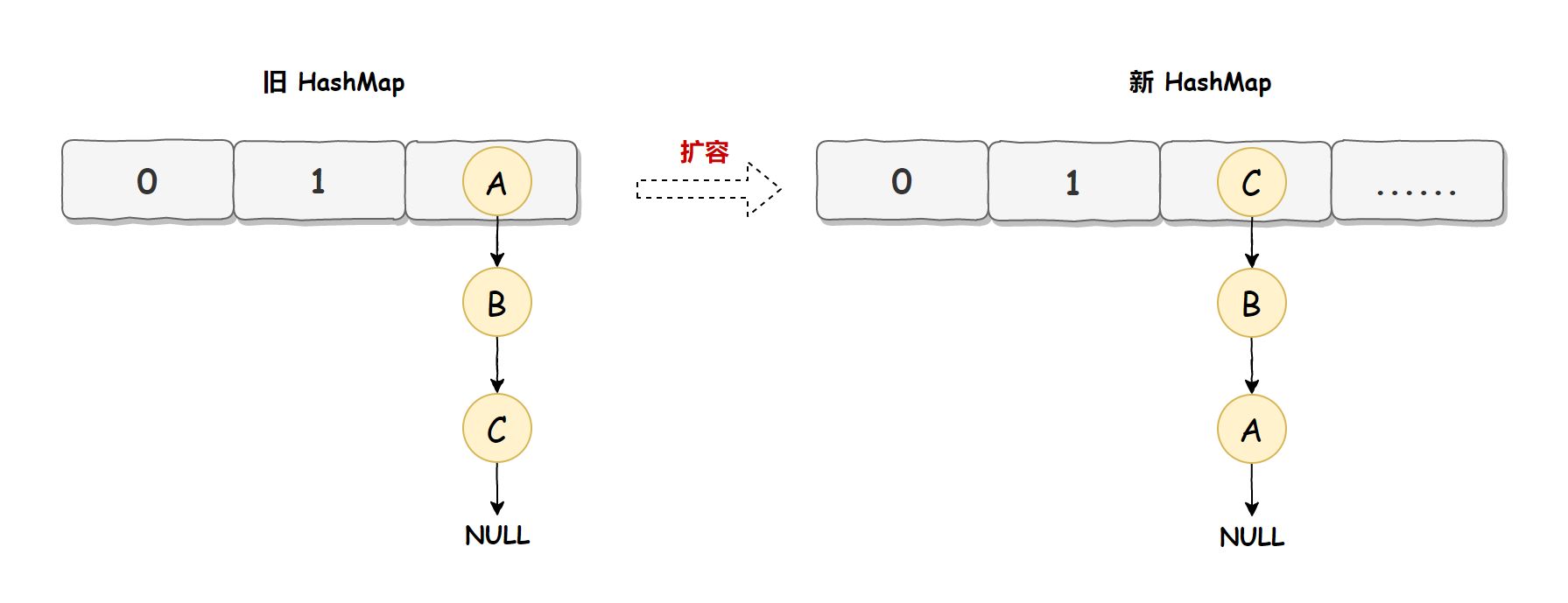
ConcurrentHashMap 原理 JDK 7 HashMap 并发死链
正常情况扩容:旧HashMap的节点会依次转移到新HashMap中,旧HashMap转移的顺序是A、B、C,而新HashMap使用的是头插法,所以最终在新HashMap中的顺序是C、B、A
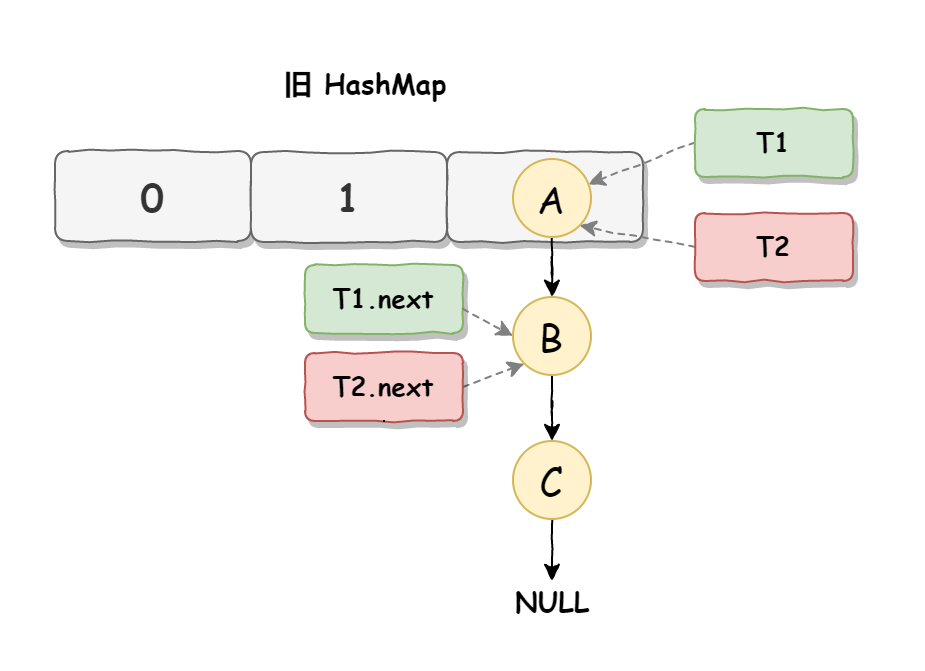
死循环执行步骤1 死循环是因为并发HashMap扩容导致的,并发扩容的第一步,线程T1和线程T2要对HashMap进行扩容操作,此时T1和T2指向的是链表的头结点元素A,而T1和T2的下一个节点,也就是T1.next和T2.next指向的是B节点
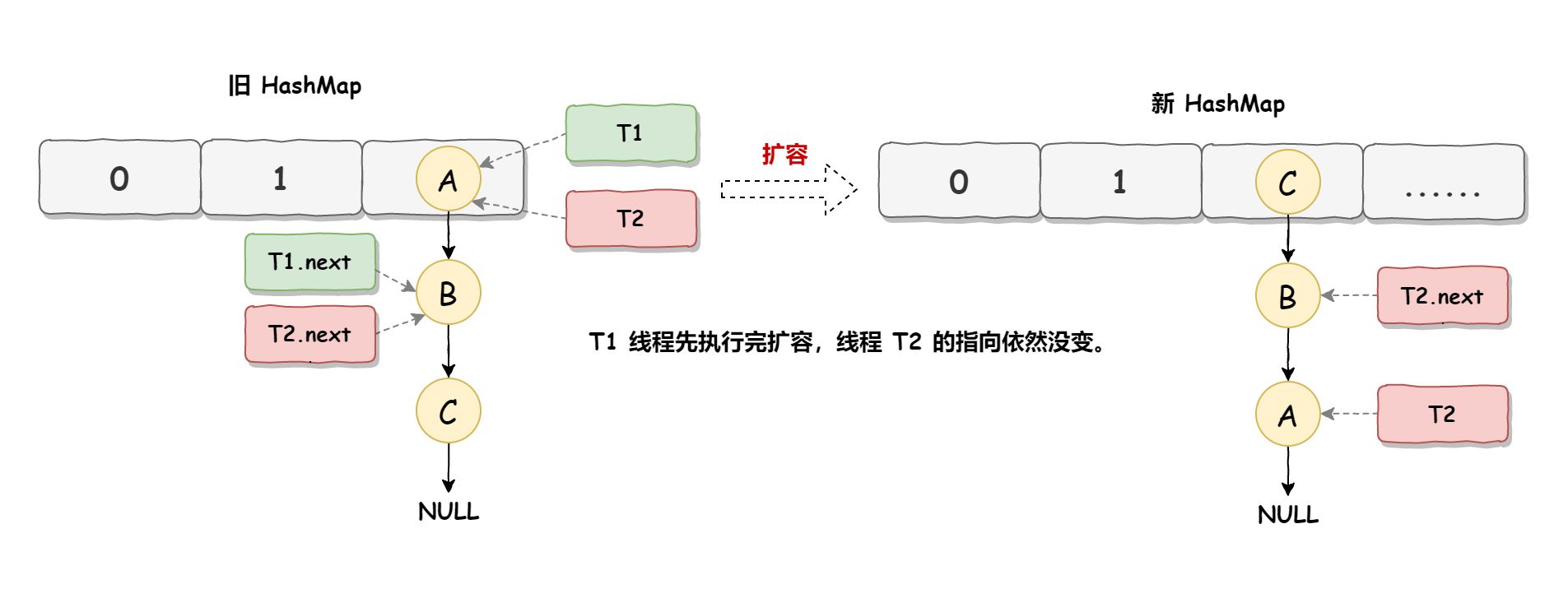
死循环执行步骤2 死循环的第二步操作是,线程T2时间片用完进入休眠状态,而线程T1开始执行扩容操作,一直到线程T1扩容完成后,线程T2才被唤醒,扩容之后的场景如下图所示:
从上图可知线程T1执行之后,因为是头插法,所以HashMap的顺序已经发生了改变,但线程T2对于发生的一切是不可知的,所以它的指向元素依然没变,如上图展示的那样,T2指向的是A元素,T2.next指向的节点是B元素。
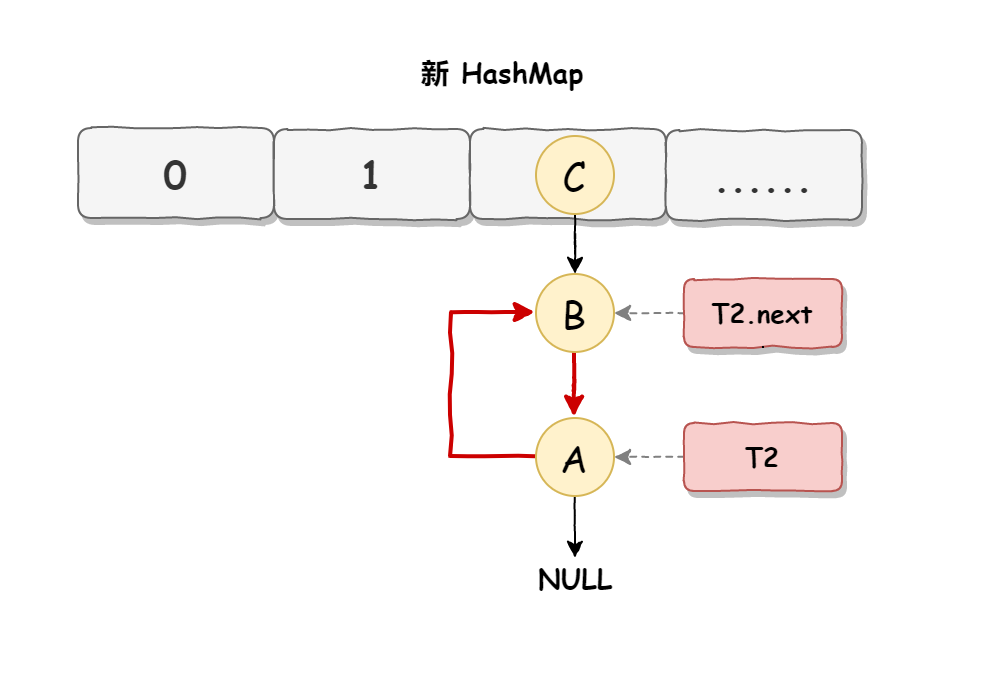
死循环执行步骤3 当线程T1执行完,而线程T2恢复执行时,死循环就建立了,如下图所示:
因为T1执行完扩容之后B节点的下一个节点是A,而T2线程指向的首节点是A,第二个节点是B,这个顺序刚好和T1扩完容完之后的节点顺序是相反的。T1执行完之后的顺序是B到A,而T2的顺序是A到B,这样A节点和B节点就形成死循环了 ,这就是HashMap死循环导致的原因。
测试代码 注意
要在 JDK 7 下运行,否则扩容机制和 hash 的计算方法都变了
以下测试代码是精心准备的,不要随便改动
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 public static void main (String[] args) { System.out.println("长度为16时,桶下标为1的key" ); for (int i = 0 ; i < 64 ; i++) { if (hash(i) % 16 == 1 ) { System.out.println(i); } } System.out.println("长度为32时,桶下标为1的key" ); for (int i = 0 ; i < 64 ; i++) { if (hash(i) % 32 == 1 ) { System.out.println(i); } } final HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap <Integer, Integer>(); map.put(2 , null ); map.put(3 , null ); map.put(4 , null ); map.put(5 , null ); map.put(6 , null ); map.put(7 , null ); map.put(8 , null ); map.put(9 , null ); map.put(10 , null ); map.put(16 , null ); map.put(35 , null ); map.put(1 , null ); System.out.println("扩容前大小[main]:" +map.size()); new Thread () { @Override public void run () { map.put(50 , null ); System.out.println("扩容后大小[Thread-0]:" +map.size()); } }.start(); new Thread () { @Override public void run () { map.put(50 , null ); System.out.println("扩容后大小[Thread-1]:" +map.size()); } }.start(); } final static int hash (Object k) { int h = 0 ; if (0 != h && k instanceof String) { return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k); } h ^= k.hashCode(); h ^= (h >>> 20 ) ^ (h >>> 12 ); return h ^ (h >>> 7 ) ^ (h >>> 4 ); }
死链复现 调试工具使用 idea
在 HashMap 源码 590 行加断点
1 int newCapacity = newTable.length;
断点的条件如下,目的是让 HashMap 在扩容为 32 时,并且线程为 Thread-0 或 Thread-1 时停下来
1 2 3 4 5 newTable.length==32 && ( Thread.currentThread().getName().equals("Thread-0" )|| Thread.currentThread().getName().equals("Thread-1" ) )
断点暂停方式选择 Thread,否则在调试 Thread-0 时,Thread-1 无法恢复运行
运行代码,程序在预料的断点位置停了下来,输出
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 长度为16 时,桶下标为1 的key 1 16 35 50 长度为32 时,桶下标为1 的key 1 35 扩容前大小[main]:12
接下来进入扩容流程调试
在 HashMap 源码 594 行加断点
1 2 3 Entry<K,V> next = e.next; if (rehash)
这是为了观察 e 节点和 next 节点的状态,Thread-0 单步执行到 594 行,再 594 处再添加一个断点(条件Thread.currentThread().getName().equals(“Thread-0”))
这时可以在 Variables 面板观察到 e 和 next 变量,使用 view as -> Object 查看节点状态
1 2 e (1 )->(35 )->(16 )->null next (35 ) ->(16 )->null
在 Threads 面板选中 Thread-1 恢复运行,可以看到控制台输出新的内容如下,Thread-1 扩容已完成
1 2 newTable[1] (35)->(1)->null 扩容后大小:13
这时 Thread-0 还停在 594 处, Variables 面板变量的状态已经变化为
1 2 e (1 )->null next (35 ) ->(1 )->null
为什么呢,因为 Thread-1 扩容时链表也是后加入的元素放入链表头,因此链表就倒过来了,但 Thread-1 虽然结果正确,但它结束后 Thread-0 还要继续运行
接下来就可以单步调试(F8)观察死链的产生了
下一轮循环到 594,将 e 搬迁到 newTable 链表头
1 2 3 newTable[1 ] (1 )->null e (35 ) ->(1 )->null next (1 ) ->null
下一轮循环到 594,将 e 搬迁到 newTable 链表头
1 2 3 newTable[1 ] (35 )->(1 )->null e (1 ) ->null next null
再看看源码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 e.next = newTable[1 ]; newTable[1 ] = e; e = next;
源码分析 HashMap 的并发死链发生在扩容时
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 void transfer (Entry[] newTable, boolean rehash) { int newCapacity = newTable.length; for (Entry<K,V> e : table) { while (null != e) { Entry<K,V> next = e.next; if (rehash) { e.hash = null == e.key ? 0 : hash(e.key); } int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity); e.next = newTable[i]; newTable[i] = e; e = next; } } }
假设 map 中初始元素是
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 原始链表,格式:[下标] (key,next) [1 ] (1 ,35 )->(35 ,16 )->(16 ,null ) 线程 a 执行到 1 处 ,此时局部变量 e 为 (1 ,35 ),而局部变量 next 为 (35 ,16 ) 线程 a 挂起 线程 b 开始执行 第一次循环 [1 ] (1 ,null ) 第二次循环 [1 ] (35 ,1 )->(1 ,null ) 第三次循环 [1 ] (35 ,1 )->(1 ,null ) [17 ] (16 ,null ) 切换回线程 a,此时局部变量 e 和 next 被恢复,引用没变但内容变了:e 的内容被改为 (1 ,null ),而 next 的内 容被改为 (35 ,1 ) 并链向 (1 ,null ) 第一次循环 [1 ] (1 ,null ) 第二次循环,注意这时 e 是 (35 ,1 ) 并链向 (1 ,null ) 所以 next 又是 (1 ,null ) [1 ] (35 ,1 )->(1 ,null ) 第三次循环,e 是 (1 ,null ),而 next 是 null ,但 e 被放入链表头,这样 e.next 变成了 35 (2 处) [1 ] (1 ,35 )->(35 ,1 )->(1 ,35 ) 已经是死链了
小结
究其原因,是因为在多线程环境下使用了非线程安全的 map 集合
JDK 8 虽然将扩容算法做了调整,不再将元素加入链表头(而是保持与扩容前一样的顺序),但仍不意味着能够在多线程环境下能够安全扩容,还会出现其它问题(如扩容丢数据)
JDK 8 ConcurrentHashMap 重要属性和内部类 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 private transient volatile int sizeCtl;static class Node <K,V> implements Map .Entry<K,V> {}transient volatile Node<K,V>[] table;private transient volatile Node<K,V>[] nextTable;static final class ForwardingNode <K,V> extends Node <K,V> {}static final class ReservationNode <K,V> extends Node <K,V> {}static final class TreeBin <K,V> extends Node <K,V> {}static final class TreeNode <K,V> extends Node <K,V> {}
重要方法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 static final <K,V> Node<K,V> tabAt (Node<K,V>[] tab, int i) static final <K,V> boolean casTabAt (Node<K,V>[] tab, int i, Node<K,V> c, Node<K,V> v) static final <K,V> void setTabAt (Node<K,V>[] tab, int i, Node<K,V> v)
构造器分析 可以看到实现了懒惰初始化 ,在构造方法中仅仅计算了 table 的大小,以后在第一次使用时才会真正创建
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public ConcurrentHashMap (int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, int concurrencyLevel) { if (!(loadFactor > 0.0f ) || initialCapacity < 0 || concurrencyLevel <= 0 ) throw new IllegalArgumentException (); if (initialCapacity < concurrencyLevel) initialCapacity = concurrencyLevel; long size = (long )(1.0 + (long )initialCapacity / loadFactor); int cap = (size >= (long )MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : tableSizeFor((int )size); this .sizeCtl = cap; }
get 流程 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public V get (Object key) { Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> e, p; int n, eh; K ek; int h = spread(key.hashCode()); if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && (e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1 ) & h)) != null ) { if ((eh = e.hash) == h) { if ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek))) return e.val; } else if (eh < 0 ) return (p = e.find(h, key)) != null ? p.val : null ; while ((e = e.next) != null ) { if (e.hash == h && ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) return e.val; } } return null ; }
put 流程 以下数组简称(table),链表简称(bin)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 public V put (K key, V value) { return putVal(key, value, false ); } final V putVal (K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) { if (key == null || value == null ) throw new NullPointerException (); int hash = spread(key.hashCode()); int binCount = 0 ; for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) { Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh; if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0 ) tab = initTable(); else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1 ) & hash)) == null ) { if (casTabAt(tab, i, null , new Node <K,V>(hash, key, value, null ))) break ; } else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED) tab = helpTransfer(tab, f); else { V oldVal = null ; synchronized (f) { if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) { if (fh >= 0 ) { binCount = 1 ; for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) { K ek; if (e.hash == hash && ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) { oldVal = e.val; if (!onlyIfAbsent) e.val = value; break ; } Node<K,V> pred = e; if ((e = e.next) == null ) { pred.next = new Node <K,V>(hash, key, value, null ); break ; } } } else if (f instanceof TreeBin) { Node<K,V> p; binCount = 2 ; if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key, value)) != null ) { oldVal = p.val; if (!onlyIfAbsent) p.val = value; } } } } if (binCount != 0 ) { if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD) treeifyBin(tab, i); if (oldVal != null ) return oldVal; break ; } } } addCount(1L , binCount); return null ; } private final Node<K,V>[] initTable() { Node<K,V>[] tab; int sc; while ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0 ) { if ((sc = sizeCtl) < 0 ) Thread.yield(); else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this , SIZECTL, sc, -1 )) { try { if ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0 ) { int n = (sc > 0 ) ? sc : DEFAULT_CAPACITY; Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node <?,?>[n]; table = tab = nt; sc = n - (n >>> 2 ); } } finally { sizeCtl = sc; } break ; } } return tab; } private final void addCount (long x, int check) { CounterCell[] as; long b, s; if ( (as = counterCells) != null || !U.compareAndSwapLong(this , BASECOUNT, b = baseCount, s = b + x) ) { CounterCell a; long v; int m; boolean uncontended = true ; if ( as == null || (m = as.length - 1 ) < 0 || (a = as[ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe() & m]) == null || !(uncontended = U.compareAndSwapLong(a, CELLVALUE, v = a.value, v + x)) ) { fullAddCount(x, uncontended); return ; } if (check <= 1 ) return ; s = sumCount(); } if (check >= 0 ) { Node<K,V>[] tab, nt; int n, sc; while (s >= (long )(sc = sizeCtl) && (tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) { int rs = resizeStamp(n); if (sc < 0 ) { if ((sc >>> RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) != rs || sc == rs + 1 || sc == rs + MAX_RESIZERS || (nt = nextTable) == null || transferIndex <= 0 ) break ; if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this , SIZECTL, sc, sc + 1 )) transfer(tab, nt); } else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this , SIZECTL, sc, (rs << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) + 2 )) transfer(tab, null ); s = sumCount(); } } }
size 计算流程 size 计算实际发生在 put,remove 改变集合元素的操作之中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public int size () { long n = sumCount(); return ((n < 0L ) ? 0 : (n > (long )Integer.MAX_VALUE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : (int )n); } final long sumCount () { CounterCell[] as = counterCells; CounterCell a; long sum = baseCount; if (as != null ) { for (int i = 0 ; i < as.length; ++i) { if ((a = as[i]) != null ) sum += a.value; } } return sum; }
Java 8 数组(Node) +( 链表 Node | 红黑树 TreeNode ) 以下数组简称(table),链表简称(bin)
初始化,使用 cas 来保证并发安全,懒惰初始化 table
树化,当 table.length < 64 时,先尝试扩容,超过 64 时,并且 bin.length > 8 时,会将链表树化,树化过程会用 synchronized 锁住链表头
put,如果该 bin 尚未创建,只需要使用 cas 创建 bin;如果已经有了,锁住链表头进行后续 put 操作,元素添加至 bin 的尾部
get,无锁操作仅需要保证可见性,扩容过程中 get 操作拿到的是 ForwardingNode 它会让 get 操作在新 table 进行搜索
扩容,扩容时以 bin 为单位进行,需要对 bin 进行 synchronized,但这时妙的是其它竞争线程也不是无事可做,它们会帮助把其它 bin 进行扩容,扩容时平均只有 1/6 的节点会把复制到新 table 中
size,元素个数保存在 baseCount 中,并发时的个数变动保存在 CounterCell[] 当中。最后统计数量时累加即可
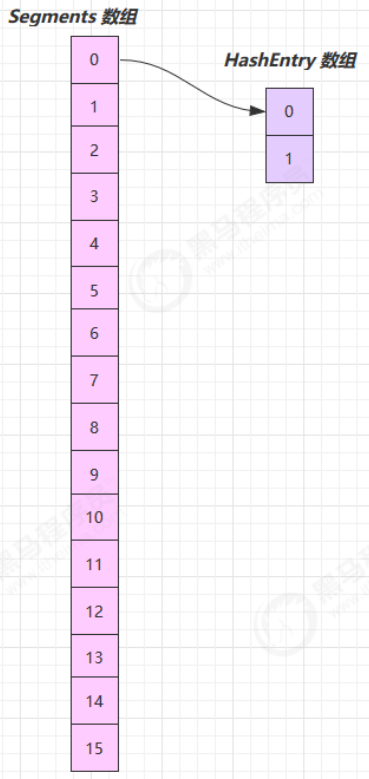
JDK 7 ConcurrentHashMap 它维护了一个 segment 数组,每个 segment 对应一把锁
优点:如果多个线程访问不同的 segment,实际是没有冲突的,这与 jdk8 中是类似的
缺点:Segments 数组默认大小为16,这个容量初始化指定后就不能改变了,并且不是懒惰初始化
构造器分析 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 public ConcurrentHashMap (int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, int concurrencyLevel) { if (!(loadFactor > 0 ) || initialCapacity < 0 || concurrencyLevel <= 0 ) throw new IllegalArgumentException (); if (concurrencyLevel > MAX_SEGMENTS) concurrencyLevel = MAX_SEGMENTS; int sshift = 0 ; int ssize = 1 ; while (ssize < concurrencyLevel) { ++sshift; ssize <<= 1 ; } this .segmentShift = 32 - sshift; this .segmentMask = ssize - 1 ; if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY; int c = initialCapacity / ssize; if (c * ssize < initialCapacity) ++c; int cap = MIN_SEGMENT_TABLE_CAPACITY; while (cap < c) cap <<= 1 ; Segment<K,V> s0 = new Segment <K,V>(loadFactor, (int )(cap * loadFactor), (HashEntry<K,V>[])new HashEntry [cap]); Segment<K,V>[] ss = (Segment<K,V>[])new Segment [ssize]; UNSAFE.putOrderedObject(ss, SBASE, s0); this .segments = ss; }
构造完成,如下图所示
可以看到 ConcurrentHashMap 没有实现懒惰初始化,空间占用不友好
其中 this.segmentShift 和 this.segmentMask 的作用是决定将 key 的 hash 结果匹配到哪个 segment
例如,根据某一 hash 值求 segment 位置,先将高位向低位移动 this.segmentShift 位
put 流程 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public V put (K key, V value) { Segment<K,V> s; if (value == null ) throw new NullPointerException (); int hash = hash(key); int j = (hash >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask; if ((s = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObject (segments, (j << SSHIFT) + SBASE)) == null ) { s = ensureSegment(j); } return s.put(key, hash, value, false ); }
segment 继承了可重入锁(ReentrantLock),它的 put 方法为
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 final V put (K key, int hash, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) { HashEntry<K,V> node = tryLock() ? null : scanAndLockForPut(key, hash, value); V oldValue; try { HashEntry<K,V>[] tab = table; int index = (tab.length - 1 ) & hash; HashEntry<K,V> first = entryAt(tab, index); for (HashEntry<K,V> e = first;;) { if (e != null ) { K k; if ((k = e.key) == key || (e.hash == hash && key.equals(k))) { oldValue = e.value; if (!onlyIfAbsent) { e.value = value; ++modCount; } break ; } e = e.next; } else { if (node != null ) node.setNext(first); else node = new HashEntry <K,V>(hash, key, value, first); int c = count + 1 ; if (c > threshold && tab.length < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) rehash(node); else setEntryAt(tab, index, node); ++modCount; count = c; oldValue = null ; break ; } } } finally { unlock(); } return oldValue; }
rehash 流程 发生在 put 中,因为此时已经获得了锁,因此 rehash 时不需要考虑线程安全
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 private void rehash (HashEntry<K,V> node) { HashEntry<K,V>[] oldTable = table; int oldCapacity = oldTable.length; int newCapacity = oldCapacity << 1 ; threshold = (int )(newCapacity * loadFactor); HashEntry<K,V>[] newTable = (HashEntry<K,V>[]) new HashEntry [newCapacity]; int sizeMask = newCapacity - 1 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < oldCapacity ; i++) { HashEntry<K,V> e = oldTable[i]; if (e != null ) { HashEntry<K,V> next = e.next; int idx = e.hash & sizeMask; if (next == null ) newTable[idx] = e; else { HashEntry<K,V> lastRun = e; int lastIdx = idx; for (HashEntry<K,V> last = next; last != null ; last = last.next) { int k = last.hash & sizeMask; if (k != lastIdx) { lastIdx = k; lastRun = last; } } newTable[lastIdx] = lastRun; for (HashEntry<K,V> p = e; p != lastRun; p = p.next) { V v = p.value; int h = p.hash; int k = h & sizeMask; HashEntry<K,V> n = newTable[k]; newTable[k] = new HashEntry <K,V>(h, p.key, v, n); } } } } int nodeIndex = node.hash & sizeMask; node.setNext(newTable[nodeIndex]); newTable[nodeIndex] = node; table = newTable; }
附,调试代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 public static void main (String[] args) { ConcurrentHashMap<Integer, String> map = new ConcurrentHashMap <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < 1000 ; i++) { int hash = hash(i); int segmentIndex = (hash >>> 28 ) & 15 ; if (segmentIndex == 4 && hash % 8 == 2 ) { System.out.println(i + "\t" + segmentIndex + "\t" + hash % 2 + "\t" + hash % 4 + "\t" + hash % 8 ); } } map.put(1 , "value" ); map.put(15 , "value" ); map.put(169 , "value" ); map.put(197 , "value" ); map.put(341 , "value" ); map.put(484 , "value" ); map.put(545 , "value" ); map.put(912 , "value" ); map.put(941 , "value" ); System.out.println("ok" ); } private static int hash (Object k) { int h = 0 ; if ((0 != h) && (k instanceof String)) { return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k); } h ^= k.hashCode(); h += (h << 15 ) ^ 0xffffcd7d ; h ^= (h >>> 10 ); h += (h << 3 ); h ^= (h >>> 6 ); h += (h << 2 ) + (h << 14 ); int v = h ^ (h >>> 16 ); return v; }
get 流程 get 时并未加锁,用了 UNSAFE 方法保证了可见性,扩容过程中,get 先发生就从旧表取内容,get 后发生就从新表取内容
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public V get (Object key) { Segment<K,V> s; HashEntry<K,V>[] tab; int h = hash(key); long u = (((h >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask) << SSHIFT) + SBASE; if ((s = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(segments, u)) != null && (tab = s.table) != null ) { for (HashEntry<K,V> e = (HashEntry<K,V>) UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile (tab, ((long )(((tab.length - 1 ) & h)) << TSHIFT) + TBASE); e != null ; e = e.next) { K k; if ((k = e.key) == key || (e.hash == h && key.equals(k))) return e.value; } } return null ; }
size 计算流程
计算元素个数前,先不加锁计算两次,如果前后两次结果如一样,认为个数正确返回
如果不一样,进行重试,重试次数超过 3,将所有 segment 锁住,重新计算个数返回
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 public int size () { final Segment<K,V>[] segments = this .segments; int size; boolean overflow; long sum; long last = 0L ; int retries = -1 ; try { for (;;) { if (retries++ == RETRIES_BEFORE_LOCK) { for (int j = 0 ; j < segments.length; ++j) ensureSegment(j).lock(); } sum = 0L ; size = 0 ; overflow = false ; for (int j = 0 ; j < segments.length; ++j) { Segment<K,V> seg = segmentAt(segments, j); if (seg != null ) { sum += seg.modCount; int c = seg.count; if (c < 0 || (size += c) < 0 ) overflow = true ; } } if (sum == last) break ; last = sum; } } finally { if (retries > RETRIES_BEFORE_LOCK) { for (int j = 0 ; j < segments.length; ++j) segmentAt(segments, j).unlock(); } } return overflow ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : size; }
BlockingQueue (Linked )BlockingQueue 原理 基本的入队出队 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public class LinkedBlockingQueue <E> extends AbstractQueue <E> implements BlockingQueue <E>, java.io.Serializable { static class Node <E> { E item; Node<E> next; Node(E x) { item = x; } } }
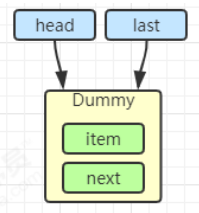
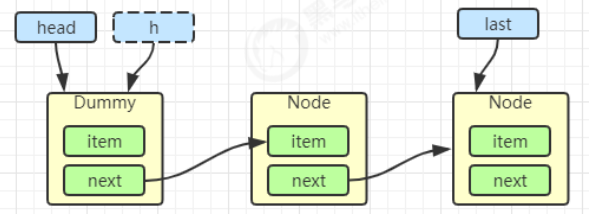
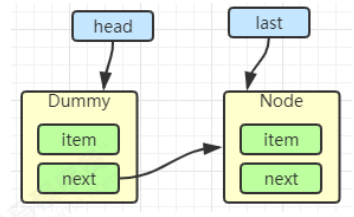
初始化链表 last = head = new Node<E>(null); Dummy 节点用来占位,item 为 null
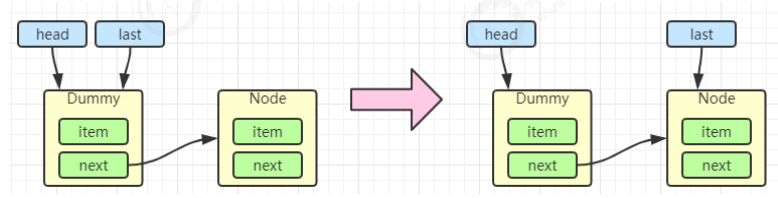
当一个节点入队 last = last.next = node;
再来一个节点入队 last = last.next = node;
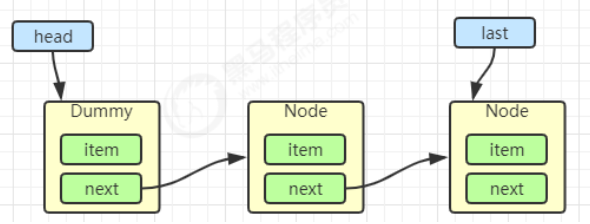
出队
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Node<E> h = head; Node<E> first = h.next; h.next = h; head = first; E x = first.item;first.item = null ; return x;h = head
1 2 3 E x = first.item;first.item = null ; return x;
加锁分析 高明之处在于用了两把锁和 dummy 节点
线程安全分析
当节点总数大于 2 时(包括 dummy 节点),putLock 保证的是 last 节点的线程安全,takeLock 保证的是 head 节点的线程安全。两把锁保证了入队和出队没有竞争
当节点总数等于 2 时(即一个 dummy 节点,一个正常节点)这时候,仍然是两把锁锁两个对象,不会竞争
当节点总数等于 1 时(就一个 dummy 节点)这时 take 线程会被 notEmpty 条件阻塞,有竞争,会阻塞
1 2 3 4 5 private final ReentrantLock putLock = new ReentrantLock ();private final ReentrantLock takeLock = new ReentrantLock ();
put 操作 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 public void put (E e) throws InterruptedException { if (e == null ) throw new NullPointerException (); int c = -1 ; Node<E> node = new Node <E>(e); final ReentrantLock putLock = this .putLock; final AtomicInteger count = this .count; putLock.lockInterruptibly(); try { while (count.get() == capacity) { notFull.await(); } enqueue(node); c = count.getAndIncrement(); if (c + 1 < capacity) notFull.signal(); } finally { putLock.unlock(); } if (c == 0 ) signalNotEmpty(); }
take 操作 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 public E take () throws InterruptedException { E x; int c = -1 ; final AtomicInteger count = this .count; final ReentrantLock takeLock = this .takeLock; takeLock.lockInterruptibly(); try { while (count.get() == 0 ) { notEmpty.await(); } x = dequeue(); c = count.getAndDecrement(); if (c > 1 ) notEmpty.signal(); } finally { takeLock.unlock(); } if (c == capacity) signalNotFull() return x; }
由 put 唤醒 put 是为了避免信号不足
性能比较 主要列举 LinkedBlockingQueue 与 ArrayBlockingQueue 的性能比较
Linked 支持有界,Array 强制有界
Linked 实现是链表,Array 实现是数组
Linked 是懒惰的,而 Array 需要提前初始化 Node 数组
Linked 每次入队会生成新 Node,而 Array 的 Node 是提前创建好的
Linked 两把锁,Array 一把锁
ConcurrentLinkedQueue ConcurrentLinkedQueue 的设计与 LinkedBlockingQueue 非常像,也是
两把【锁】,同一时刻,可以允许两个线程同时(一个生产者与一个消费者)执行
dummy 节点的引入让两把【锁】将来锁住的是不同对象,避免竞争
只是这【锁】使用了 cas 来实现
事实上,ConcurrentLinkedQueue 应用还是非常广泛的
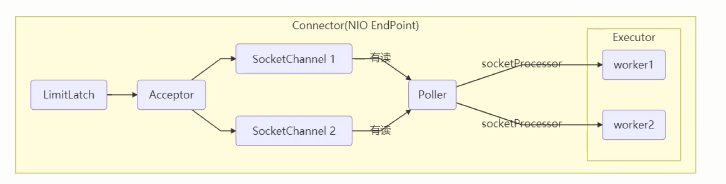
例如之前讲的 Tomcat 的 Connector 结构时,Acceptor 作为生产者向 Poller 消费者传递事件信息时,正是采用了ConcurrentLinkedQueue 将 SocketChannel 给 Poller 使用
ConcurrentLinkedQueue 原理 模仿 ConcurrentLinkedQueue 初始代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 package cn.itcast.concurrent.thirdpart.test;import java.util.Collection;import java.util.Iterator;import java.util.Queue;import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicReference;public class Test3 { public static void main (String[] args) { MyQueue<String> queue = new MyQueue <>(); queue.offer("1" ); queue.offer("2" ); queue.offer("3" ); System.out.println(queue); } } class MyQueue <E> implements Queue <E> { @Override public String toString () { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder (); for (Node<E> p = head; p != null ; p = p.next.get()) { E item = p.item; if (item != null ) { sb.append(item).append("->" ); } } sb.append("null" ); return sb.toString(); } @Override public int size () { return 0 ; } @Override public boolean isEmpty () { return false ; } @Override public boolean contains (Object o) { return false ; } @Override public Iterator<E> iterator () { return null ; } @Override public Object[] toArray() { return new Object [0 ]; } @Override public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) { return null ; } @Override public boolean add (E e) { return false ; } @Override public boolean remove (Object o) { return false ; } @Override public boolean containsAll (Collection<?> c) { return false ; } @Override public boolean addAll (Collection<? extends E> c) { return false ; } @Override public boolean removeAll (Collection<?> c) { return false ; } @Override public boolean retainAll (Collection<?> c) { return false ; } @Override public void clear () { } @Override public E remove () { return null ; } @Override public E element () { return null ; } @Override public E peek () { return null ; } public MyQueue () { head = last = new Node <>(null , null ); } private volatile Node<E> last; private volatile Node<E> head; private E dequeue () { return null ; } @Override public E poll () { return null ; } @Override public boolean offer (E e) { return true ; } static class Node <E> { volatile E item; public Node (E item, Node<E> next) { this .item = item; this .next = new AtomicReference <>(next); } AtomicReference<Node<E>> next; } }
offer方法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public boolean offer (E e) { Node<E> n = new Node <>(e, null ); while (true ) { AtomicReference<Node<E>> next = last.next; if (next.compareAndSet(null , n)) { last = n; return true ; } } }
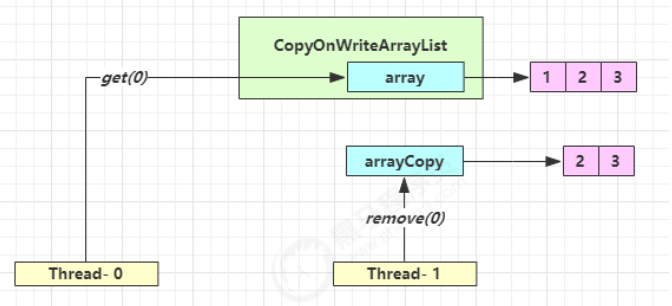
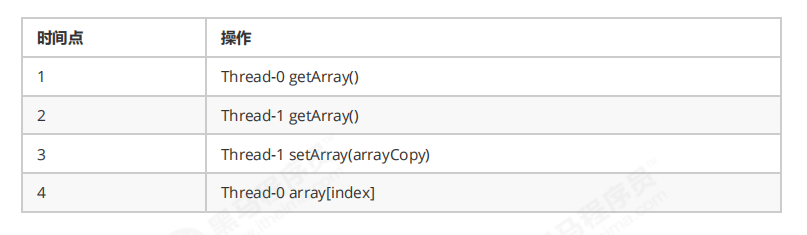
CopyOnWriteArrayList 底层实现采用了 写入时拷贝 的思想,增删改操作会将底层数组拷贝一份,更改操作在新数组上执行,这时不影响其它线程的并发读 ,读写分离 。CopyOnWriteArraySet 底层对 CopyOnWriteArrayList 进行了包装,装饰器模式。 以新增为例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public boolean add (E e) { synchronized (lock) { Object[] es = getArray(); int len = es.length; es = Arrays.copyOf(es, len + 1 ); es[len] = e; setArray(es); return true ; } }
这里的源码版本是 Java 11,在 Java 1.8 中使用的是可重入锁而不是 synchronized
其它读操作并未加锁,例如:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public void forEach (Consumer<? super E> action) { Objects.requireNonNull(action); for (Object x : getArray()) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) x; action.accept(e); } }
适合『读多写少』的应用场景
get 弱一致性
不容易测试,但问题确实存在
迭代器弱一致性 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 CopyOnWriteArrayList<Integer> list = new CopyOnWriteArrayList <>(); list.add(1 ); list.add(2 ); list.add(3 ); Iterator<Integer> iter = list.iterator(); new Thread (() -> { list.remove(0 ); System.out.println(list); }).start(); sleep1s(); while (iter.hasNext()) { System.out.println(iter.next()); }
不要觉得弱一致性就不好
数据库的 MVCC 都是弱一致性的表现
并发高和一致性是矛盾的,需要权衡
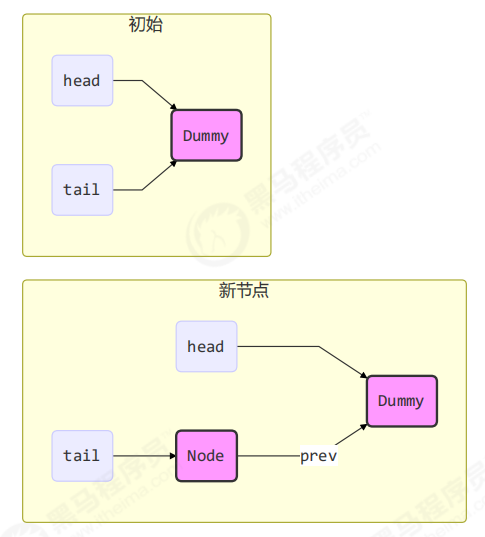
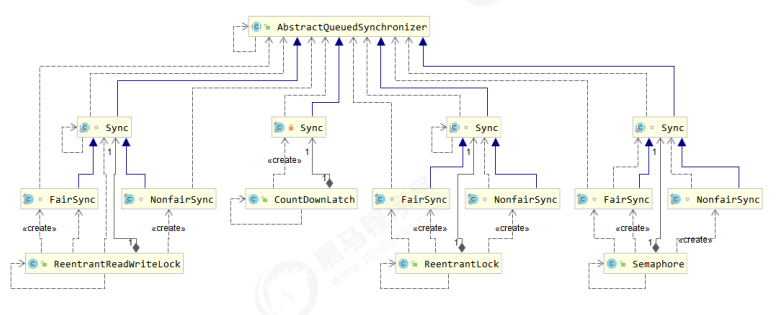
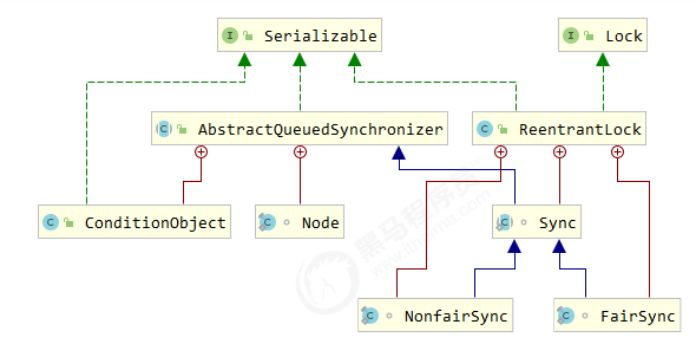 ·
·