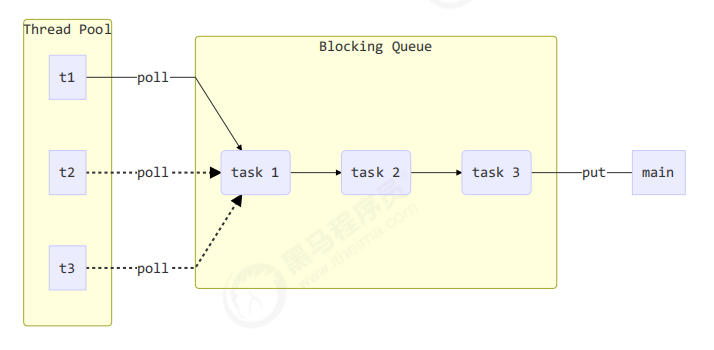
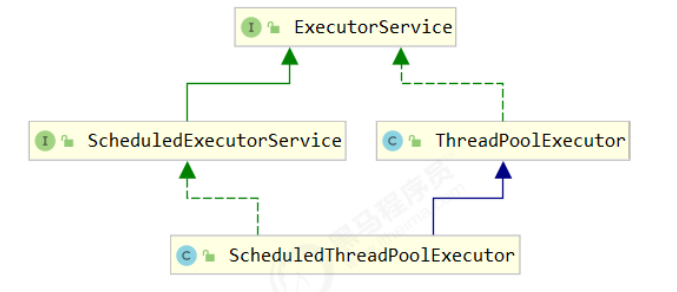
自定义线程池
可重用线程 (消费者:不断获取任务来执行)+阻塞队列 (生产者消费者模式下平衡速度差异的组件)+main (生产者:源源不断生成任务)
步骤1:自定义拒绝策略接口 RejectPolicy 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 package com.tobestronger.n8._8_1;@FunctionalInterface interface RejectPolicy <T> { void reject (BlockingQueue<T> queue, T task) ; }
步骤2:自定义任务队列 BlockingQueue 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 package com.tobestronger.n8._8_1;import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;import java.util.ArrayDeque;import java.util.Deque;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;@Slf4j(topic = "c.BlockingQueue") class BlockingQueue <T> { private Deque<T> queue = new ArrayDeque <>(); private ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock (); private Condition fullWaitSet = lock.newCondition(); private Condition emptyWaitSet = lock.newCondition(); private int capcity; public BlockingQueue (int capcity) { log.info("构造BlockingQueue" ); this .capcity = capcity; } public T poll (long timeout, TimeUnit unit) { lock.lock(); try { long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout); while (queue.isEmpty()) { try { if (nanos <= 0 ) { return null ; } nanos = emptyWaitSet.awaitNanos(nanos); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } T t = queue.removeFirst(); fullWaitSet.signal(); return t; } finally { lock.unlock(); } } public T take () { lock.lock(); try { while (queue.isEmpty()) { try { emptyWaitSet.await(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } T t = queue.removeFirst(); fullWaitSet.signal(); return t; } finally { lock.unlock(); } } public void put (T task) { lock.lock(); try { while (queue.size() == capcity) { try { log.debug("等待加入任务队列 {} ..." , task); fullWaitSet.await(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } log.debug("加入任务队列 {}" , task); queue.addLast(task); emptyWaitSet.signal(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } } public boolean offer (T task, long timeout, TimeUnit timeUnit) { lock.lock(); try { long nanos = timeUnit.toNanos(timeout); while (queue.size() == capcity) { try { if (nanos <= 0 ) { return false ; } log.debug("等待加入任务队列 {} ..." , task); nanos = fullWaitSet.awaitNanos(nanos); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } log.debug("加入任务队列 {}" , task); queue.addLast(task); emptyWaitSet.signal(); return true ; } finally { lock.unlock(); } } public int size () { lock.lock(); try { return queue.size(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } } public void tryPut (RejectPolicy<T> rejectPolicy, T task) { lock.lock(); try { if (queue.size() == capcity) { log.info("队列已满,按照拒绝策略处理任务 {}" ,task); rejectPolicy.reject(this , task); } else { log.debug("队列未满,加入任务队列 {}" , task); queue.addLast(task); emptyWaitSet.signal(); } } finally { lock.unlock(); } } }
步骤3:自定义线程池 ThreadPool 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 package com.tobestronger.n8._8_1;import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;import java.util.HashSet;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;@Slf4j(topic = "c.ThreadPool") class ThreadPool { private BlockingQueue<Runnable> taskQueue; private HashSet<Worker> workers = new HashSet <>(); private int coreSize; private long timeout; private TimeUnit timeUnit; private RejectPolicy<Runnable> rejectPolicy; public void execute (Runnable task) { log.info("接收到任务需要执行: " +task); synchronized (workers) { if (workers.size() < coreSize) { log.info("coreSize未满" ); Worker worker = new Worker (task); log.debug("新增 worker {} 来执行任务 {}" , worker, task); workers.add(worker); worker.start(); } else { log.info("coreSize已经满了!!!!!,尝试先将任务放入队列 {}" ,task); taskQueue.tryPut(rejectPolicy, task); } } } public ThreadPool (int coreSize, long timeout, TimeUnit timeUnit, int queueCapcity, RejectPolicy<Runnable> rejectPolicy) { log.info("构造ThreadPool" ); this .coreSize = coreSize; this .timeout = timeout; this .timeUnit = timeUnit; this .taskQueue = new BlockingQueue <>(queueCapcity); this .rejectPolicy = rejectPolicy; } class Worker extends Thread { private Runnable task; public Worker (Runnable task) { this .task = task; } @Override public void run () { log.info("跑起来了,让我看看有没有task来做" ); while (task != null || (task = taskQueue.poll(timeout, timeUnit)) != null ) { try { log.debug("获取到任务了,正在执行...{}" , task); task.run(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { log.info("搞定一个任务 {},尝试获取新任务执行" ,task); task = null ; } } synchronized (workers) { log.debug("worker 因长时间没有可执行任务 将被释放 {}" , this ); workers.remove(this ); } } } }
步骤4:测试 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 package com.tobestronger.n8._8_1;import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestCustomThreadPool") public class TestCustomThreadPool { public static void main (String[] args) { ThreadPool threadPool = new ThreadPool (2 , 3000 , TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, 10 , (queue, task)->{ log.info("当前拒绝策略: 让调用者自己执行任务,没有开新线程,直接调用的run()" ); task.run(); }); for (int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++) { int j = i; threadPool.execute(() -> { try { log.info("我先睡1s" ); Thread.sleep(1000L ); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } log.debug("我是第 {} 个任务,我马上执行完了" , j); }); } } }
某次的执行结果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 Connected to the target VM, address: '127.0.0.1:49956' , transport: 'socket' 18 :25 :21.216 c.ThreadPool [main] - 构造ThreadPool18 :25 :21.225 c.BlockingQueue [main] - 构造BlockingQueue18 :25 :21.228 c.ThreadPool [main] - 接收到任务需要执行: com.tobestronger.n8._8_1.TestCustomThreadPool$$Lambda$2 /626742236 @1b68b9a418 :25 :21.229 c.ThreadPool [main] - coreSize未满18 :25 :21.231 c.ThreadPool [main] - 新增 worker Thread[Thread-0 ,5 ,main] 来执行任务 com.tobestronger.n8._8_1.TestCustomThreadPool$$Lambda$2 /626742236 @1b68b9a418 :25 :21.235 c.ThreadPool [main] - 接收到任务需要执行: com.tobestronger.n8._8_1.TestCustomThreadPool$$Lambda$2 /626742236 @51b7e5df18 :25 :21.236 c.ThreadPool [main] - coreSize已经满了!!!!!,尝试先将任务放入队列 com.tobestronger.n8._8_1.TestCustomThreadPool$$Lambda$2 /626742236 @51b7e5df18 :25 :21.236 c.BlockingQueue [main] - 队列未满,加入任务队列 com.tobestronger.n8._8_1.TestCustomThreadPool$$Lambda$2 /626742236 @51b7e5df18 :25 :21.236 c.ThreadPool [Thread-0 ] - 跑起来了,让我看看有没有task来做18 :25 :21.236 c.ThreadPool [main] - 接收到任务需要执行: com.tobestronger.n8._8_1.TestCustomThreadPool$$Lambda$2 /626742236 @18a70f1618 :25 :21.236 c.ThreadPool [main] - coreSize已经满了!!!!!,尝试先将任务放入队列 com.tobestronger.n8._8_1.TestCustomThreadPool$$Lambda$2 /626742236 @18a70f1618 :25 :21.236 c.BlockingQueue [main] - 队列已满,按照拒绝策略处理任务 com.tobestronger.n8._8_1.TestCustomThreadPool$$Lambda$2 /626742236 @18a70f1618 :25 :21.236 c.TestCustomThreadPool [main] - 当前拒绝策略: 让调用者自己执行任务,没有开新线程,直接调用的run()18 :25 :21.236 c.ThreadPool [Thread-0 ] - 获取到任务了,正在执行...com.tobestronger.n8._8_1.TestCustomThreadPool$$Lambda$2 /626742236 @1b68b9a418 :25 :21.236 c.TestCustomThreadPool [main] - 我先睡1s18 :25 :21.236 c.TestCustomThreadPool [Thread-0 ] - 我先睡1s18 :25 :22.236 c.TestCustomThreadPool [Thread-0 ] - 我是第 0 个任务,我马上执行完了18 :25 :22.236 c.ThreadPool [Thread-0 ] - 搞定一个任务 com.tobestronger.n8._8_1.TestCustomThreadPool$$Lambda$2 /626742236 @1b68b9a4,尝试获取新任务执行18 :25 :22.236 c.TestCustomThreadPool [main] - 我是第 2 个任务,我马上执行完了18 :25 :22.237 c.ThreadPool [Thread-0 ] - 获取到任务了,正在执行...com.tobestronger.n8._8_1.TestCustomThreadPool$$Lambda$2 /626742236 @51b7e5df18 :25 :22.237 c.TestCustomThreadPool [Thread-0 ] - 我先睡1s18 :25 :22.237 c.ThreadPool [main] - 接收到任务需要执行: com.tobestronger.n8._8_1.TestCustomThreadPool$$Lambda$2 /626742236 @62e136d318 :25 :22.237 c.ThreadPool [main] - coreSize已经满了!!!!!,尝试先将任务放入队列 com.tobestronger.n8._8_1.TestCustomThreadPool$$Lambda$2 /626742236 @62e136d318 :25 :22.237 c.BlockingQueue [main] - 队列未满,加入任务队列 com.tobestronger.n8._8_1.TestCustomThreadPool$$Lambda$2 /626742236 @62e136d318 :25 :23.238 c.TestCustomThreadPool [Thread-0 ] - 我是第 1 个任务,我马上执行完了18 :25 :23.238 c.ThreadPool [Thread-0 ] - 搞定一个任务 com.tobestronger.n8._8_1.TestCustomThreadPool$$Lambda$2 /626742236 @51b7e5df,尝试获取新任务执行18 :25 :23.238 c.ThreadPool [Thread-0 ] - 获取到任务了,正在执行...com.tobestronger.n8._8_1.TestCustomThreadPool$$Lambda$2 /626742236 @62e136d318 :25 :23.238 c.TestCustomThreadPool [Thread-0 ] - 我先睡1s18 :25 :24.239 c.TestCustomThreadPool [Thread-0 ] - 我是第 3 个任务,我马上执行完了18 :25 :24.239 c.ThreadPool [Thread-0 ] - 搞定一个任务 com.tobestronger.n8._8_1.TestCustomThreadPool$$Lambda$2 /626742236 @62e136d3,尝试获取新任务执行18 :25 :27.241 c.ThreadPool [Thread-0 ] - worker 因长时间没有可执行任务 将被释放 Thread[Thread-0 ,5 ,main]Disconnected from the target VM, address: '127.0.0.1:49956' , transport: 'socket' Process finished with exit code 0
ThreadPoolExecutor
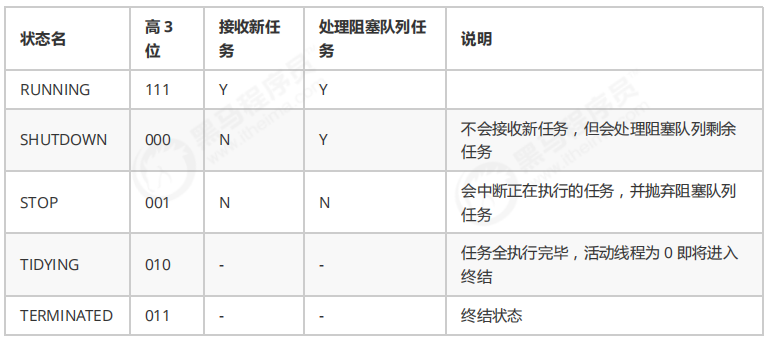
线程池状态 ThreadPoolExecutor 使用 int 的高 3 位 来表示线程池状态 ,低 29 位 表示线程数量
从数字上比较,TERMINATED > TIDYING > STOP > SHUTDOWN > RUNNING。因为第一位是符号位,RUNNING 是负数,所以最小。
这些信息存储在一个原子变量 ctl 中,目的是将线程池状态与线程个数合二为一 ,这样就可以用一次 cas 原子操作进行赋值
1 2 3 4 5 ctl.compareAndSet(c, ctlOf(targetState, workerCountOf(c)))); private static int ctlOf (int rs, int wc) { return rs | wc; }
构造方法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public ThreadPoolExecutor (int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue, ThreadFactory threadFactory, RejectedExecutionHandler handler)
corePoolSize 核心线程数目 (最多保留的线程数)
maximumPoolSize 最大线程数目
keepAliveTime 生存时间 - 针对救急线程
unit 时间单位 - 针对救急线程
workQueue 阻塞队列
threadFactory 线程工厂 - 可以为线程创建时起个好名字
handler 拒绝策略
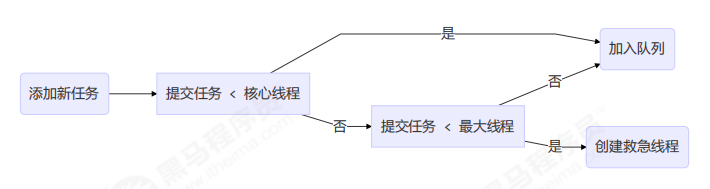
工作方式:
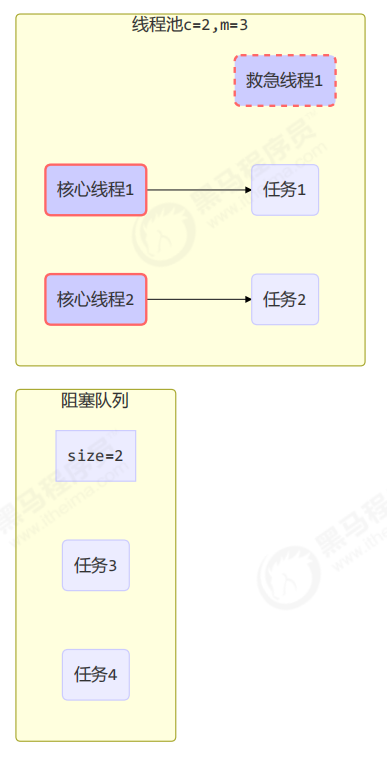
线程池中刚开始没有线程,当一个任务提交给线程池后,线程池会创建一个新线程来执行任务。
当线程数达到 corePoolSize 并没有线程空闲,这时再加入任务,新加的任务会被加入workQueue 队列排队,直到有空闲的线程。
如果队列选择了有界队列,那么任务超过了队列大小时,会创建 maximumPoolSize - corePoolSize 数目的线程来救急。
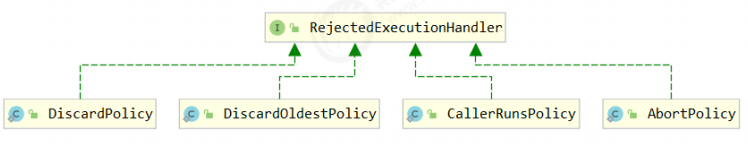
如果线程到达 maximumPoolSize 仍然有新任务这时会执行拒绝策略。拒绝策略 jdk 提供了 4 种实现,其它著名框架也提供了实现
AbortPolicy 让调用者抛出 RejectedExecutionException 异常,这是默认策略
CallerRunsPolicy 让调用者运行任务
DiscardPolicy 放弃本次任务
DiscardOldestPolicy 放弃队列中最早的任务,本任务取而代之
Dubbo 的实现,在抛出 RejectedExecutionException 异常之前会记录日志,并 dump 线程栈信息,方便定位问题
Netty 的实现,是创建一个新线程来执行任务
ActiveMQ 的实现,带超时等待(60s)尝试放入队列,类似我们之前自定义的拒绝策略
PinPoint 的实现,它使用了一个拒绝策略链,会逐一尝试策略链中每种拒绝策略
当高峰过去后,超过corePoolSize 的救急线程如果一段时间没有任务做,需要结束节省资源,这个时间由 keepAliveTime 和 unit 来控制。
根据这个构造方法,JDK Executors 类中提供了众多工厂方法来创建各种用途的线程池.
JDK Executors类中提供的工厂方法 newFixedThreadPool 1 2 3 4 5 public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool (int nThreads) { return new ThreadPoolExecutor (nThreads, nThreads, 0L , TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue <Runnable>()); }
特点
核心线程数 == 最大线程数(没有救急线程被创建),因此也无需超时时间
阻塞队列是无界的,可以放任意数量的任务
评价 适用于任务量已知,相对耗时的任务
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 @Slf4j(topic = "c.TestExecutors") public class TestExecutors { public static void main (String[] args) throws InterruptedException { test(); } private static void test () { ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2 , new ThreadFactory () { private AtomicInteger t = new AtomicInteger (1 ); @Override public Thread newThread (Runnable r) { return new Thread (r, "mypool_t" + t.getAndIncrement()); } }); pool.execute(() -> { log.debug("1" ); }); pool.execute(() -> { log.debug("2" ); }); pool.execute(() -> { log.debug("3" ); }); } }
输出
1 2 3 23 :21 :21.055 c.TestExecutors [mypool_t1] - 1 23 :21 :21.055 c.TestExecutors [mypool_t2] - 2 23 :21 :21.057 c.TestExecutors [mypool_t1] - 3
newCachedThreadPool 1 2 3 4 5 public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool () { return new ThreadPoolExecutor (0 , Integer.MAX_VALUE, 60L , TimeUnit.SECONDS, new SynchronousQueue <Runnable>()); }
特点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 SynchronousQueue<Integer> integers = new SynchronousQueue <>(); new Thread (() -> { try { log.debug("putting {} " , 1 ); integers.put(1 ); log.debug("{} putted..." , 1 ); log.debug("putting...{} " , 2 ); integers.put(2 ); log.debug("{} putted..." , 2 ); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } },"t1" ).start(); sleep(1 ); new Thread (() -> { try { log.debug("taking {}" , 1 ); integers.take(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } },"t2" ).start(); sleep(1 ); new Thread (() -> { try { log.debug("taking {}" , 2 ); integers.take(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } },"t3" ).start();
输出
1 2 3 4 5 6 11 :48 :15.500 c.TestSynchronousQueue [t1] - putting 1 11 :48 :16.500 c.TestSynchronousQueue [t2] - taking 1 11 :48 :16.500 c.TestSynchronousQueue [t1] - 1 putted... 11 :48 :16.500 c.TestSynchronousQueue [t1] - putting...2 11 :48 :17.502 c.TestSynchronousQueue [t3] - taking 2 11 :48 :17.503 c.TestSynchronousQueue [t1] - 2 putted...
评价
整个线程池表现为线程数会根据任务量不断增长,没有上限,当任务执行完毕,空闲 1分钟后释放线程。
适合任务数比较密集,但每个任务执行时间较短的情况
newSingleThreadExecutor 1 2 3 4 5 6 public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor () { return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService (new ThreadPoolExecutor (1 , 1 , 0L , TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue <Runnable>())); }
使用场景: 多个任务串行
希望多个任务排队执行。线程数固定为 1,任务数多于 1 时,会放入无界队列排队。任务执行完毕,这唯一的线程也不会被释放。
和自己创建一个线程来工作的区别:
和 Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1) 的区别
(用于)提交任务(的几个方法) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 void execute (Runnable command) ;<T> Future<T> submit (Callable<T> task) ; <T> List<Future<T>> invokeAll (Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks) throws InterruptedException; <T> List<Future<T>> invokeAll (Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException; <T> T invokeAny (Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException; <T> T invokeAny (Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException;
submit 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 @Slf4j(topic = "c.TestSubmit") public class TestSubmit { public static void main (String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2 ); method(pool); } private static void method (ExecutorService pool) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { Future<String> future = pool.submit(() -> { log.debug("running" ); Thread.sleep(1000 ); return "ok" ; }); log.debug("{}" , future.get()); } }
输出
1 2 23 :32 :38.087 c.TestSubmit [pool-1 -thread-1 ] - running23 :32 :39.090 c.TestSubmit [main] - ok
invokeAll 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 @Slf4j(topic = "c.TestSubmit") public class TestSubmit { public static void main (String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2 ); method(pool); } private static void method (ExecutorService pool) throws InterruptedException { List<Future<String>> futures = pool.invokeAll(Arrays.asList( () -> { log.debug("begin" ); Thread.sleep(1000 ); return "1" ; }, () -> { log.debug("begin" ); Thread.sleep(500 ); return "2" ; }, () -> { log.debug("begin" ); Thread.sleep(2000 ); return "3" ; } )); futures.forEach( f -> { try { log.debug("{}" , f.get()); } catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); } }
输出
1 2 3 4 5 6 23 :35 :23.987 c.TestSubmit [pool-1 -thread-2 ] - begin23 :35 :23.987 c.TestSubmit [pool-1 -thread-1 ] - begin23 :35 :24.503 c.TestSubmit [pool-1 -thread-2 ] - begin23 :35 :26.519 c.TestSubmit [main] - 1 23 :35 :26.520 c.TestSubmit [main] - 2 23 :35 :26.520 c.TestSubmit [main] - 3
invokeAny 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 @Slf4j(topic = "c.TestSubmit") public class TestSubmit { public static void main (String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2 ); method(pool); } private static void method (ExecutorService pool) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { String result = pool.invokeAny(Arrays.asList( () -> { log.debug("begin 1" ); Thread.sleep(1000 ); log.debug("end 1" ); return "1" ; }, () -> { log.debug("begin 2" ); Thread.sleep(500 ); log.debug("end 2" ); return "2" ; }, () -> { log.debug("begin 3" ); Thread.sleep(2000 ); log.debug("end 3" ); return "3" ; } )); log.debug("{}" , result); }
输出
1 2 3 4 5 23 :36 :38.269 c.TestSubmit [pool-1 -thread-2 ] - begin 2 23 :36 :38.269 c.TestSubmit [pool-1 -thread-1 ] - begin 1 23 :36 :38.772 c.TestSubmit [pool-1 -thread-2 ] - end 2 23 :36 :38.772 c.TestSubmit [pool-1 -thread-2 ] - begin 3 23 :36 :38.772 c.TestSubmit [main] - 2
(用于)关闭线程池(的方法) shutdown 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 void shutdown () ;public void shutdown () { final ReentrantLock mainLock = this .mainLock; mainLock.lock(); try { checkShutdownAccess(); advanceRunState(SHUTDOWN); interruptIdleWorkers(); onShutdown(); } finally { mainLock.unlock(); } tryTerminate(); }
shutdownNow 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 List<Runnable> shutdownNow () ; public List<Runnable> shutdownNow () { List<Runnable> tasks; final ReentrantLock mainLock = this .mainLock; mainLock.lock(); try { checkShutdownAccess(); advanceRunState(STOP); interruptWorkers(); tasks = drainQueue(); } finally { mainLock.unlock(); } tryTerminate(); return tasks; }
其它方法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 boolean isShutdown () ;boolean isTerminated () ;boolean awaitTermination (long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException;
(异步)模式之(工作线程) Worker Thread 定义 让有限的工作线程(Worker Thread)来轮流异步处理无限多的任务。也可以将其归类为分工模式,它的典型实现就是线程池,也体现了经典设计模式中的享元模式。
例如,海底捞的服务员(线程),轮流处理每位客人的点餐(任务),如果为每位客人都配一名专属的服务员,那么成本就太高了(对比另一种多线程设计模式:Thread-Per-Message)
注意,不同任务类型应该使用不同的线程池,这样能够避免饥饿,并能提升效率
例如,如果一个餐馆的工人既要招呼客人(任务类型A),又要到后厨做菜(任务类型B)显然效率不咋地,分成服务员(线程池A)与厨师(线程池B)更为合理,当然你能想到更细致的分工
饥饿 固定大小线程池会有饥饿现象
两个工人是同一个线程池中的两个线程
他们要做的事情是:为客人点餐和到后厨做菜,这是两个阶段的工作
比如工人A 处理了点餐任务,接下来它要等着 工人B 把菜做好,然后上菜,他俩也配合的蛮好
但现在同时来了两个客人,这个时候工人A 和工人B 都去处理点餐了,这时没人做饭了,饥饿
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 public class TestStarvation { static final List<String> MENU = Arrays.asList("地三鲜" , "宫保鸡丁" , "辣子鸡丁" , "烤鸡翅" ); static Random RANDOM = new Random (); static String cooking () { return MENU.get(RANDOM.nextInt(MENU.size())); } public static void main (String[] args) { ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2 ); executorService.execute(() -> { log.debug("处理点餐..." ); Future<String> f = executorService.submit(() -> { log.debug("做菜" ); return cooking(); }); try { log.debug("上菜: {}" , f.get()); } catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); } }
输出
1 2 3 17 :21 :27.883 c.TestDeadLock [pool-1 -thread-1 ] - 处理点餐...17 :21 :27.891 c.TestDeadLock [pool-1 -thread-2 ] - 做菜17 :21 :27.891 c.TestDeadLock [pool-1 -thread-1 ] - 上菜: 烤鸡翅
当注释取消后,可能的输出
1 2 17 :08:41.339 c.TestDeadLock [pool-1 -thread-2 ] - 处理点餐... 17 :08:41.339 c.TestDeadLock [pool-1 -thread-1 ] - 处理点餐...
解决方法可以增加线程池的大小,不过不是根本解决方案,还是前面提到的,不同的任务类型,采用不同的线程池,例如:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 public class TestStarvation { static final List<String> MENU = Arrays.asList("地三鲜" , "宫保鸡丁" , "辣子鸡丁" , "烤鸡翅" ); static Random RANDOM = new Random (); static String cooking () { return MENU.get(RANDOM.nextInt(MENU.size())); } public static void main (String[] args) { ExecutorService waiterPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1 ); ExecutorService cookPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1 ); waiterPool.execute(() -> { log.debug("处理点餐..." ); Future<String> f = cookPool.submit(() -> { log.debug("做菜" ); return cooking(); }); try { log.debug("上菜: {}" , f.get()); } catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); waiterPool.execute(() -> { log.debug("处理点餐..." ); Future<String> f = cookPool.submit(() -> { log.debug("做菜" ); return cooking(); }); try { log.debug("上菜: {}" , f.get()); } catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); } }
输出
1 2 3 4 5 6 17 :25 :14.626 c.TestDeadLock [pool-1 -thread-1 ] - 处理点餐... 17 :25 :14.630 c.TestDeadLock [pool-2 -thread-1 ] - 做菜17 :25 :14.631 c.TestDeadLock [pool-1 -thread-1 ] - 上菜: 地三鲜17 :25 :14.632 c.TestDeadLock [pool-1 -thread-1 ] - 处理点餐... 17 :25 :14.632 c.TestDeadLock [pool-2 -thread-1 ] - 做菜17 :25 :14.632 c.TestDeadLock [pool-1 -thread-1 ] - 上菜: 辣子鸡丁
创建多少线程池合适
过小会导致程序不能充分地利用系统资源、容易导致饥饿
过大会导致更多的线程上下文切换,占用更多内存
CPU 密集型运算 通常采用 cpu 核数 + 1 能够实现最优的 CPU 利用率,+1 是保证当线程由于页缺失故障(操作系统)或其它原因导致暂停时,额外的这个线程就能顶上去,保证 CPU 时钟周期不被浪费
I/O 密集型运算 CPU 不总是处于繁忙状态,例如,当你执行业务计算时,这时候会使用 CPU 资源,但当你执行 I/O 操作时、远程 RPC 调用时,包括进行数据库操作时,这时候 CPU 就闲下来了,你可以利用多线程提高它的利用率。
经验公式如下
1 线程数 = 核数 * 期望 CPU 利用率 * 总时间(CPU计算时间+等待时间) / CPU 计算时间
例如 4 核 CPU 计算时间是 50% ,其它等待时间是 50%,期望 cpu 被 100% 利用,套用公式
1 4 * 100% * 100% / 50% = 8
例如 4 核 CPU 计算时间是 10% ,其它等待时间是 90%,期望 cpu 被 100% 利用,套用公式
1 4 * 100% * 100% / 10% = 40
任务调度线程池 ScheduledExecutorService java.util.Timer 在『任务调度线程池』功能加入之前,可以使用 java.util.Timer 来实现定时功能,Timer 的优点在于简单易用 ,但由于所有任务都是由同一个线程来调度,因此所有任务都是串行执行 的,同一时间只能有一个任务在执行,前一个任务的延迟或异常 都将会影响到之后的任务。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public static void main (String[] args) { Timer timer = new Timer (); TimerTask task1 = new TimerTask () { @Override public void run () { log.debug("task 1" ); sleep(2 ); } }; TimerTask task2 = new TimerTask () { @Override public void run () { log.debug("task 2" ); } }; log.debug("start..." ); timer.schedule(task1, 1000 ); timer.schedule(task2, 1000 ); }
输出
1 2 3 20 :58 :36.945 c.TestTimer [main] - start...20 :58 :37.953 c.TestTimer [Timer-0 ] - task 1 20 :58 :39.966 c.TestTimer [Timer-0 ] - task 2
ScheduledExecutorService 使用 ScheduledExecutorService 改写:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 ScheduledExecutorService executor = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(2 );executor.schedule(() -> { System.out.println("任务1,执行时间:" + new Date ()); try { Thread.sleep(2000 ); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } }, 1000 , TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); executor.schedule(() -> { System.out.println("任务2,执行时间:" + new Date ()); }, 1000 , TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
输出
1 2 任务1 ,执行时间:Thu Jan 03 12 :45 :17 CST 2019 任务2 ,执行时间:Thu Jan 03 12 :45 :17 CST 2019
scheduleAtFixedRate 方法 间隔固定时间执行任务
1 2 3 4 5 6 ScheduledExecutorService pool = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1 );log.debug("start..." ); pool.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> { log.debug("running..." ); }, 1 , 1 , TimeUnit.SECONDS);
输出
1 2 3 4 5 21 :45 :43.167 c.TestTimer [main] - start... 21 :45 :44.215 c.TestTimer [pool-1 -thread-1 ] - running... 21 :45 :45.215 c.TestTimer [pool-1 -thread-1 ] - running... 21 :45 :46.215 c.TestTimer [pool-1 -thread-1 ] - running... 21 :45 :47.215 c.TestTimer [pool-1 -thread-1 ] - running...
scheduleAtFixedRate 例子(任务执行时间超过了间隔时间 ):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 ScheduledExecutorService pool = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1 );log.debug("start..." ); pool.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> { log.debug("running..." ); sleep(2 ); }, 1 , 1 , TimeUnit.SECONDS);
输出分析:一开始,延时 1s,接下来,由于任务执行时间 > 间隔时间,间隔被『撑』到了 2s
1 2 3 4 5 21 :44 :30.311 c.TestTimer [main] - start... 21 :44 :31.360 c.TestTimer [pool-1 -thread-1 ] - running... 21 :44 :33.361 c.TestTimer [pool-1 -thread-1 ] - running... 21 :44 :35.362 c.TestTimer [pool-1 -thread-1 ] - running... 21 :44 :37.362 c.TestTimer [pool-1 -thread-1 ] - running...
scheduleWithFixedDelay 方法 1 2 3 4 5 6 ScheduledExecutorService pool = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1 );log.debug("start..." ); pool.scheduleWithFixedDelay(()-> { log.debug("running..." ); sleep(2 ); }, 1 , 1 , TimeUnit.SECONDS);
输出分析:一开始,延时 1s,scheduleWithFixedDelay 的间隔是 上一个任务结束 <-> 延时 <-> 下一个任务开始 所以间隔都是 3s
1 2 3 4 5 21 :40 :55.078 c.TestTimer [main] - start... 21 :40 :56.140 c.TestTimer [pool-1 -thread-1 ] - running... 21 :40 :59.143 c.TestTimer [pool-1 -thread-1 ] - running... 21 :41 :02.145 c.TestTimer [pool-1 -thread-1 ] - running... 21 :41 :05.147 c.TestTimer [pool-1 -thread-1 ] - running...
评价
整个线程池表现为:线程数固定,任务数多于线程数时,会放入无界队列排队。任务执行完毕,这些线程也不会被释放。用来执行延迟或反复执行的任务
正确处理执行任务异常 方法1:主动捉异常 try…catch…
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1 );pool.submit(() -> { try { log.debug("task1" ); int i = 1 / 0 ; } catch (Exception e) { log.error("error:" , e); } });
输出
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 21 :59 :04.558 c.TestTimer [pool-1 -thread-1 ] - task1 21 :59 :04.562 c.TestTimer [pool-1 -thread-1 ] - error: java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero at cn.itcast.n8.TestTimer.lambda$main$0 (TestTimer.java:28 ) at java.util.concurrent.Executors$RunnableAdapter.call(Executors.java:511 ) at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.run(FutureTask.java:266 ) at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1149 ) at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:624 ) at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:748 )
方法2:使用 Future 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1 );Future<Boolean> f = pool.submit(() -> { log.debug("task1" ); int i = 1 / 0 ; return true ; }); log.debug("result:{}" , f.get());
输出
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 21 :54 :58.208 c.TestTimer [pool-1 -thread-1 ] - task1 Exception in thread "main" java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException: java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.report(FutureTask.java:122 ) at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.get(FutureTask.java:192 ) at cn.itcast.n8.TestTimer.main(TestTimer.java:31 ) Caused by: java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero at cn.itcast.n8.TestTimer.lambda$main$0 (TestTimer.java:28 ) at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.run(FutureTask.java:266 ) at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1149 ) at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:624 ) at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:748 )
应用之定时任务 定期执行 如何让每周四 18:00:00 定时执行任务?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();LocalDateTime thursday = now.with(DayOfWeek.THURSDAY).withHour(18 ).withMinute(0 ).withSecond(0 ).withNano(0 ); if (now.compareTo(thursday) >= 0 ) { thursday = thursday.plusWeeks(1 ); } long initialDelay = Duration.between(now, thursday).toMillis();long oneWeek = 7 * 24 * 3600 * 1000 ;ScheduledExecutorService executor = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(2 );System.out.println("开始时间:" + new Date ()); executor.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> { System.out.println("执行时间:" + new Date ()); }, initialDelay, oneWeek, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
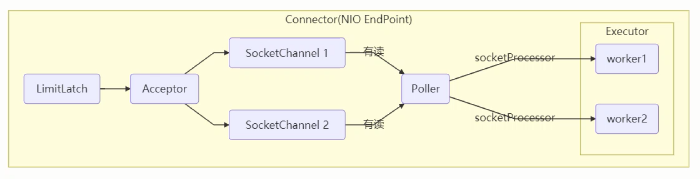
Tomcat (的)线程池(策略) Tomcat 在哪里用到了线程池呢
LimitLatch 用来限流,可以控制最大连接个数,类似 J.U.C 中的 Semaphore 后面再讲
Acceptor 只负责【接收新的 socket 连接】
Poller 只负责监听 socket channel 是否有【可读的 I/O 事件】
一旦可读,封装一个任务对象(socketProcessor),提交给 Executor 线程池处理
Executor 线程池中的工作线程最终负责【处理请求】
扩展了 ThreadPoolExecutor Tomcat 线程池扩展了 ThreadPoolExecutor,行为稍有不同
源码 tomcat-7.0.42
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public void execute (Runnable command, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) { submittedCount.incrementAndGet(); try { super .execute(command); } catch (RejectedExecutionException rx) { if (super .getQueue() instanceof TaskQueue) { final TaskQueue queue = (TaskQueue)super .getQueue(); try { if (!queue.force(command, timeout, unit)) { submittedCount.decrementAndGet(); throw new RejectedExecutionException ("Queue capacity is full." ); } } catch (InterruptedException x) { submittedCount.decrementAndGet(); Thread.interrupted(); throw new RejectedExecutionException (x); } } else { submittedCount.decrementAndGet(); throw rx; } } }
TaskQueue.java 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public boolean force (Runnable o, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException { if ( parent.isShutdown() ) throw new RejectedExecutionException ( "Executor not running, can't force a command into the queue" ); return super .offer(o,timeout,unit); is rejected }
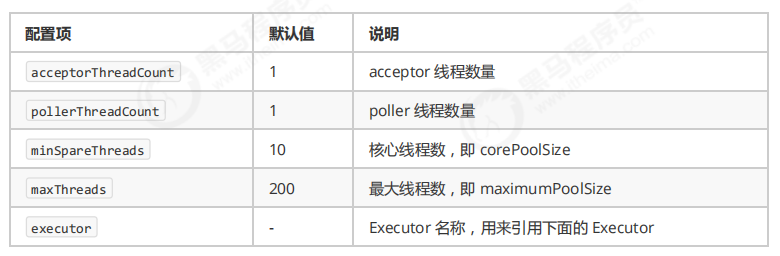
Connector 配置
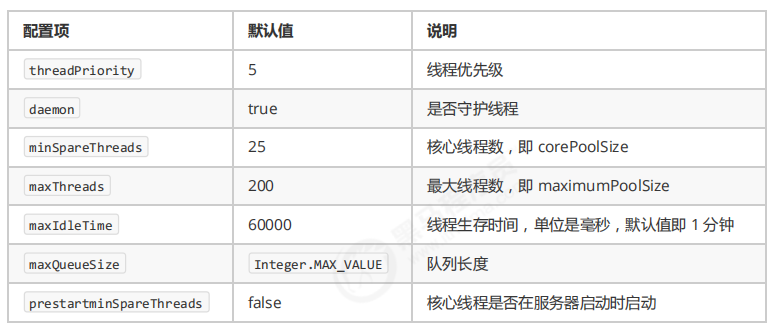
Executor 线程配置
Fork/Join (分治思想) 概念 Fork/Join 是 JDK 1.7 加入的新的线程池实现,它体现的是一种分治思想,适用于能够进行任务拆分的 cpu 密集型运算
所谓的任务拆分,是将一个大任务拆分为算法上相同的小任务,直至不能拆分可以直接求解。跟递归相关的一些计算,如归并排序、斐波那契数列 都可以用分治思想进行求解
Fork/Join 在分治的基础上加入了多线程,可以把每个任务的分解和合并交给不同的线程来完成,进一步提升了运算效率
Fork/Join 默认会创建与 cpu 核心数大小相同的线程池
使用 提交给 Fork/Join 线程池的任务需要继承 RecursiveTask(有返回值)或 RecursiveAction(没有返回值),例如下面定义了一个对 1~n 之间的整数求和的任务
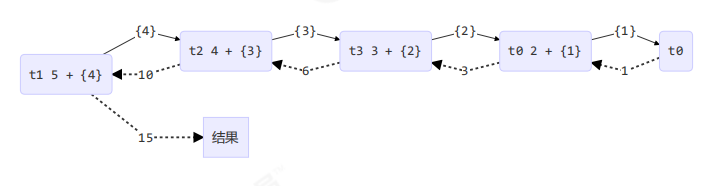
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 @Slf4j(topic = "c.TestForkJoin") public class TestForkJoin { public static void main (String[] args) { ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool (4 ); System.out.println(pool.invoke(new MyTask (5 ))); } } @Slf4j(topic = "c.MyTask") class MyTask extends RecursiveTask <Integer> { private int n; public MyTask (int n) { this .n = n; } @Override public String toString () { return "{" + n + '}' ; } @Override protected Integer compute () { if (n == 1 ) { log.debug("join() {}" , n); return n; } AddTask1 t1 = new AddTask1 (n - 1 ); t1.fork(); log.debug("fork() {} + {}" , n, t1); int result = n + t1.join(); log.debug("join() {} + {} = {}" , n, t1, result); return result; } }
结果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 [ForkJoinPool-1 -worker-0 ] - fork() 2 + {1 } [ForkJoinPool-1 -worker-1 ] - fork() 5 + {4 } [ForkJoinPool-1 -worker-0 ] - join() 1 [ForkJoinPool-1 -worker-0 ] - join() 2 + {1 } = 3 [ForkJoinPool-1 -worker-2 ] - fork() 4 + {3 } [ForkJoinPool-1 -worker-3 ] - fork() 3 + {2 } [ForkJoinPool-1 -worker-3 ] - join() 3 + {2 } = 6 [ForkJoinPool-1 -worker-2 ] - join() 4 + {3 } = 10 [ForkJoinPool-1 -worker-1 ] - join() 5 + {4 } = 15 15
用图来表示
改进
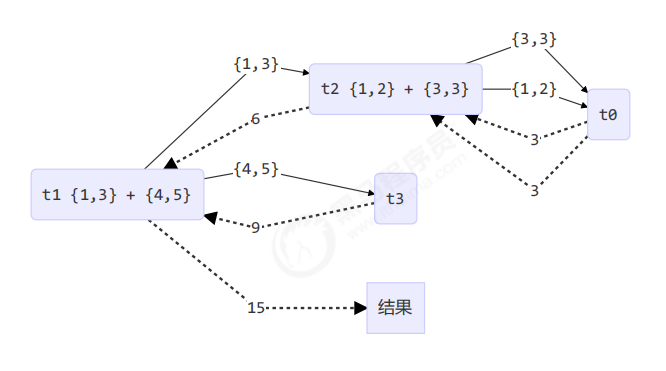
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 class AddTask3 extends RecursiveTask <Integer> { int begin; int end; public AddTask3 (int begin, int end) { this .begin = begin; this .end = end; } @Override public String toString () { return "{" + begin + "," + end + '}' ; } @Override protected Integer compute () { if (begin == end) { log.debug("join() {}" , begin); return begin; } if (end - begin == 1 ) { log.debug("join() {} + {} = {}" , begin, end, end + begin); return end + begin; } int mid = (end + begin) / 2 ; AddTask3 t1 = new AddTask3 (begin, mid); t1.fork(); AddTask3 t2 = new AddTask3 (mid + 1 , end); t2.fork(); log.debug("fork() {} + {} = ?" , t1, t2); int result = t1.join() + t2.join(); log.debug("join() {} + {} = {}" , t1, t2, result); return result; } }
然后提交给 ForkJoinPool 来执行
1 2 3 4 public static void main (String[] args) { ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool (4 ); System.out.println(pool.invoke(new AddTask3 (1 , 10 ))); }
结果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 [ForkJoinPool-1 -worker-0 ] - join() 1 + 2 = 3 [ForkJoinPool-1 -worker-3 ] - join() 4 + 5 = 9 [ForkJoinPool-1 -worker-0 ] - join() 3 [ForkJoinPool-1 -worker-1 ] - fork() {1 ,3 } + {4 ,5 } = ? [ForkJoinPool-1 -worker-2 ] - fork() {1 ,2 } + {3 ,3 } = ? [ForkJoinPool-1 -worker-2 ] - join() {1 ,2 } + {3 ,3 } = 6 [ForkJoinPool-1 -worker-1 ] - join() {1 ,3 } + {4 ,5 } = 15 15
用图来表示